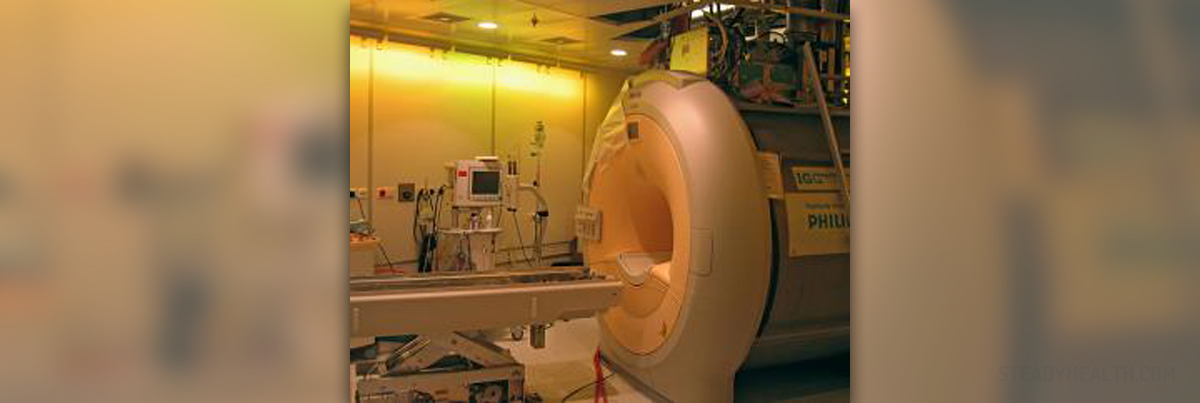
What is MRI?
MRI — or magnetic resonance imaging — is a modern radiological procedure used to examine the internal organs, skeleton, and tissues in the body with great clarity. An MRI machine looks like a large tube; the hollow space is the area where the patient will be placed for the procedure. The patient lies down on the hard surface which is slid into the tube. MRI pictures are very helpful in diagnosing a number of medical disorders. This diagnostic procedure is commonly performed in patients with multiple sclerosis, injuries of the spine, congenital deformities, aneurysm, dementia, and problems with the pituitary gland, among numerous other applications. MRI scans are also frequently used in order to test for the presence or scope of tumors or other disorders of the internal organs such as the liver, kidneys, lungs, pancreas, uterus and prostate.
What is Contrast Dye?
In a number of cases, before the MRI procedure starts, the doctor may inject a special dye into a patient's vein. This contrast dye enhances the image and helps in detecting abnormal tissue. This contrast dye contains gadolinium, which is a heavy metal. The majority of patients do not have any problems with gadolinium but in patients with severe kidney disorders, gadolinium can cause further complications.
Side Effects of Contrast Dye in MRI Scans
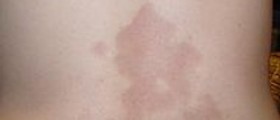
The most dangerous side effect of the contrast dye used for MRI scans is due to the gadolinium, and it is a disease called neprhogenic systemic fibrosis. This disease affects the skin, eyes, joints and internal organs. This is a painful disease which can begin soon after the MRI with contrast dye was performed or even a few months later. The first symptoms of neprhogenic systemic fibrosis include changes on the skin of the patient's arms and legs.
The color of the skin becomes pink, yellow or brown. The patient's skin can additionally change its texture and may become hard and thick. The disease can spread to the limbs and internal organs and impair their function. The other symptoms of neprhogenic systemic fibrosis include severe itching, burning sensations, and swelling of the skin, yellow spots in the eyes, joint stiffness which causes restricted movements, muscle weakness, and pain in the body. This can be a very dangerous condition which can lead to death. In some cases the patient may need a kidney transplant.
Besides neprhogenic systemic fibrosis, the patient may feel some other, often less serious, side effects as a result of contrast dye used for MRI scans. Such side effects include skin irritation, blood clots, dizziness, short breath, blood vessel inflammation and allergic reactions.
Facts you should be Familiar with
In the United States, a total of 25 cases of neprhogenic systemic fibrosis which occurred as a consequence of MRI contrast dye have been reported in the medical literature. The first injection with contrast due was given in 1988. In 1997, the first patient was diagnosed with neprhogenic systemic fibrosis. Since 2007, a warning must be placed on contrast dyes which contain gadolinium. However, before you become too worried, you should know that this complication is exceedingly rare.












_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...