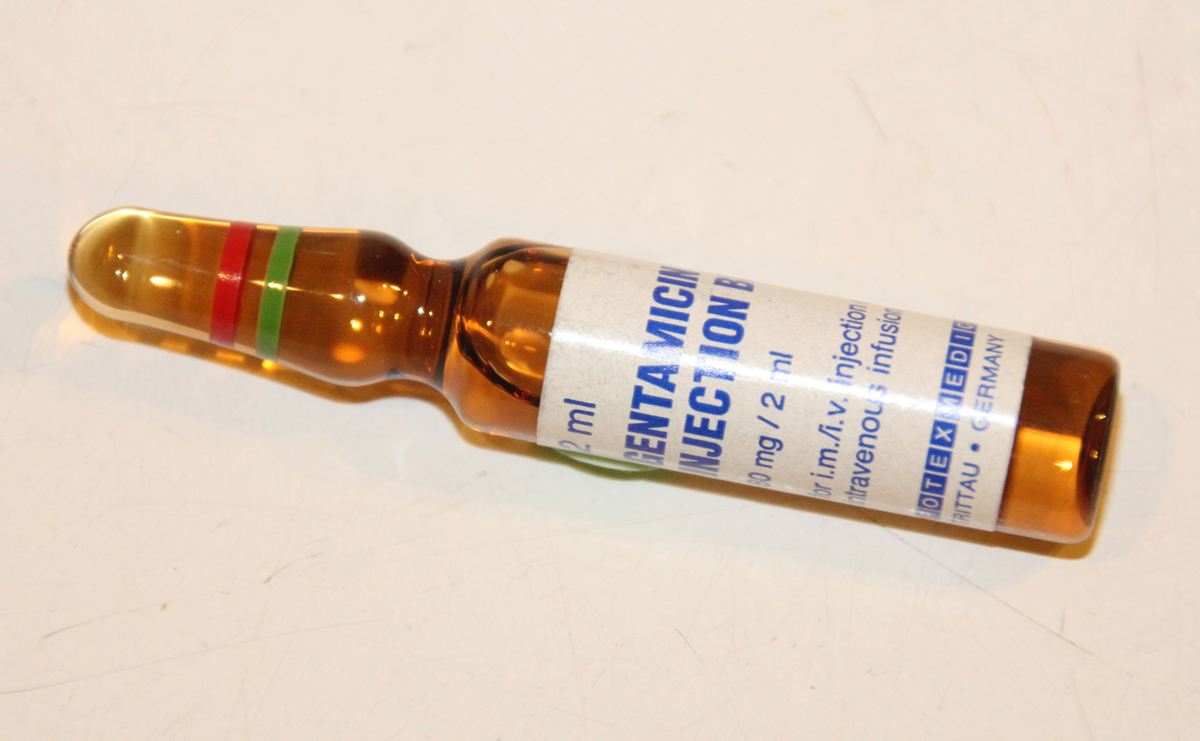
Gentamicin is an antibiotic used in the treatment of severe bacterial infections, especially the ones caused by Gram-negative bacteria. It can be taken orally, topically, intravenously, and intramuscularly.
Side Effects
The medicine has numerous side effects. Ototoxicity (the damage of the ear) and nephrotoxicity (the damage to the kidney) are the two most commonly reported side effects of gentamicin. They occur when the patients are administered gentamicin serum over a long period of time. Nephrotoxicity is more common in people suffering from renal insufficiency and can take the form of acute renal failure or azotemia. Dehydration, simultaneous use of other nephrotoxic medication, and advancing age are other risk factors for nephrotoxicity.
Ototoxicity can display no to moderate symptoms at first. An early symptom of ear toxicity is the loss of high tone hearing. Other nervous system side effects include depression, lethargy, headache, confusion, tingling skin, seizures, muscle twitching, numbness, myasthenia gravis-like syndrome, and acute organic brain syndrome. Visual acuity loss after high doses of gentamicin has also been reported. Musculoskeletal side effects have manifested as neuromuscular blockage in patients with hypocalcaemia and myasthenia gravis, as well as in cases of simultaneous use of other neuromuscular blocking substances. Joint paints, muscle weakness and tetany have also been reported.
Respiratory depression and respiratory arrest are most commonly reported respiratory side effects. Pulmonary fibrosis may also be connected to the use of gentamicin. People can also experience local reaction at the injection site, such as pain and burning. Gentamicin can also cause hypersensitivity reactions like swelling of the throat and anaphylaxis like reactions.
Gentamicin containing metabisulfite preservative has also caused allergic reactions Individuals treated with gentamicin can also have dermatologic side effects such as hives, rash, itches, alopecia and burning. Anemia, purpura, temporary agranulocytosis, leukopenia, eosinophilia, thrombocytopenia, granulocytopenia and changes in reticulocyte count are possible hematologic side effects. Hepatic side effects included the increase of LDH, transaminase serum, billirubin, and temporary hepatomegaly.
Gentamicin can also cause the blood pressure to drop orrise. Gastrointestinal tract can be adversely affected by gentamicin so that the person experiences poor appetite, nausea, vomiting, stomatitis, increased production of saliva and weight loss. Fever, temporary splenomegaly, shaking, tachycardia and rigors are other possible side effects.
Warning
As gentamicin may damage kidneys and/or nerves, the functioning of kidneys and the concentration of the drug in the blood must be under doctor’s supervision. The doctor should be contacted in cases of dizziness, tingling skin, twitching muscles, hearing loss or seizures, as they might indicate nerve damage.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...