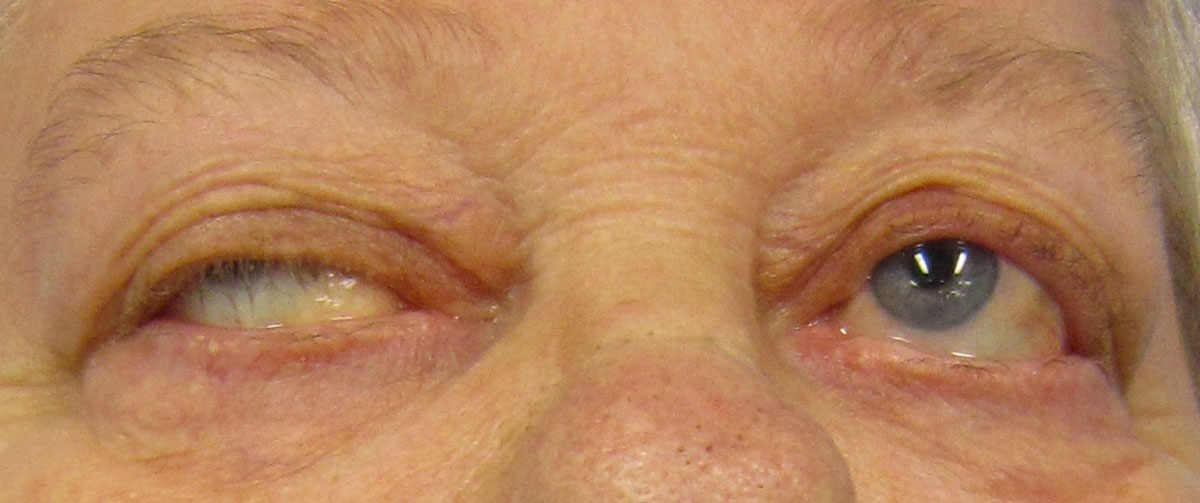
Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune neuromuscular disease that typically affects voluntary muscles and features with muscle weakness and fatigue. In myasthenia gravis antibodies affect acetylcholine receptors not allowing neurotransmitter acetylcholine to attach to these receptors and perform its duty. Improper function of acetylcholine results in weakness of muscles.
The actual etiology of myasthenia gravis is still a mystery. Some scientists believe that certain infective agents such as, viruses or bacteria may be triggers of the disease. In some patients hyperactivity of the thymus has be related to the onset of the disease. And finally, some think disease can be inherited.
Symptoms of Myasthenia Gravis
The leading symptom of myasthenia gravis is weakness of muscles. The disease usually starts with weakness of eye muscles. If there are no additional symptoms this form of myasthenia gravis is known as ocular myasthenia gravis. Apart from weakness of eye muscles patients commonly complain about double vision, droopy eyelids and in rather rare cases photophobia.
Apart from eye muscles the disease may also affect the muscles involved in swallowing causing serious problems with swallowing. The progression of the disease affects other muscles in the body. It has been reported that weakness tends to be more intensive at night, during summer and in case of infections. Fatigue and low energy levels regularly accompany weakness of muscles. The speech in some patients may be slurred.
Diagnosis of Myasthenia Gravis
The doctor may assume that the patient is suffering from myasthenia gravis if he/ she complains about weakness of muscle without accompanying pain in muscles.
Further steps of setting of the definitive diagnosis include physical examination, blood tests ( they may show the presence of anti acetylcholine antibodies) and electromyography. CT scan may visualize the presence of tumor in the thymus gland.
Treatment for Myasthenia Gravis
There are several treatment modalities for patients suffering from myasthenia gravis. Each patient requires specific approach and each of them responds differently to certain treatment option. The basic concept includes administration of anticholinesterase medications such as neostigmine and pyridostigmine. The most common side effects of anticholinesterase medications are excessive production of saliva and involuntary muscle twitching. Gastrointestinal problems such as pain in the abdomen, nausea and/or diarrhea may occur as well. Furthermore, patients may be prescribed corticosteroids (prednisone) which are due to suppress antibodies. Corticosteroids have numerous side effects and they eventually occur since these medications are usually given for a long period of time. And finally, some patients suffering from myasthenia gravis are treated with immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and cyclophosphamide.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...