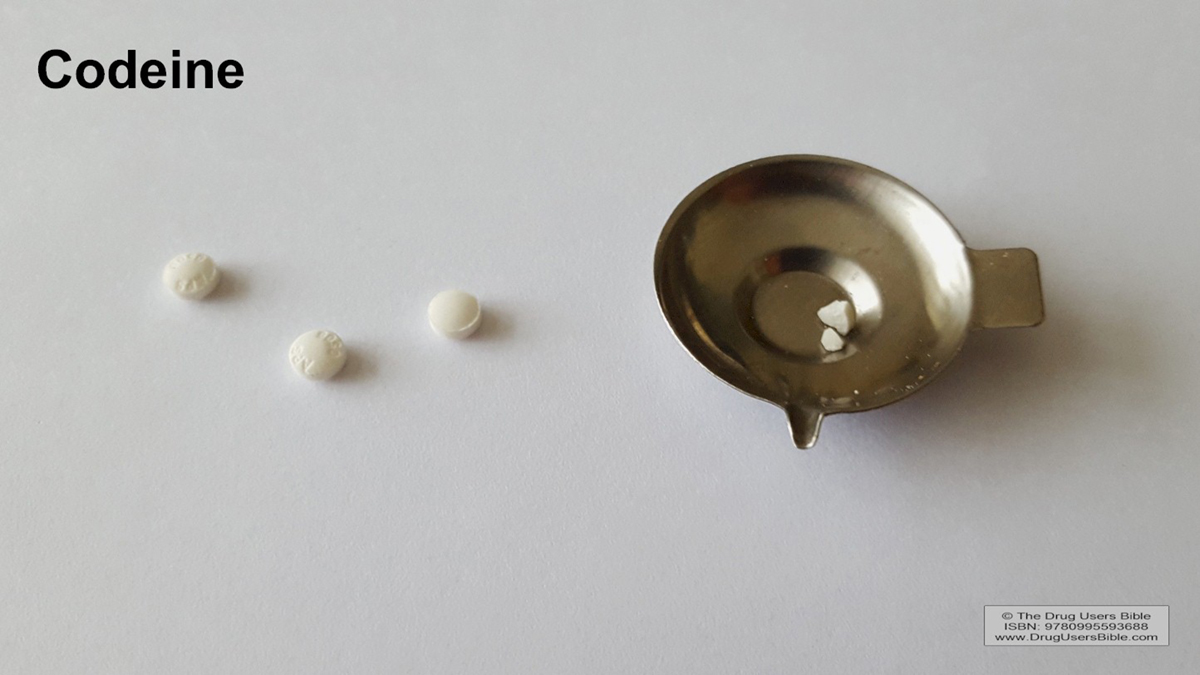

Introduction
Codeine is a narcotic pain medication and is commonly used for the relief of mild to moderate pain. Sometimes it can be used for the certain other purposes. Codeine should only be used when prescribed because it can easily form a habit. Those who have a history of drug addiction and abuse should definitely avoid codeine. Alcohol should not be combined with any narcotic pain medications because it may be fatal in certain cases. Codeine is known for sometimes triggering certain side effects which lead to impaired reactions and thinking, so one must be careful when driving or performing any action that requires alertness. Codeine therapy should never be stopped suddenly because it usually triggers some rather unpleasant withdrawal symptoms.
People who may have had any allergic reactions to narcotic medications such as morphine, vicodin, darvocet, Oxycontin, methadone, Percocet and Lortab should not take codeine. Those who suffer from paralytic ileus or asthma should also avoid codeine. If a person suffers from certain other conditions, it is strongly recommended to avoid codeine as well. Those conditions include liver disease, spine curvature, breathing disorders, underactive thyroid, gallbladder disease, adrenal gland disorders, low blood pressure, brain tumor, head injuries, kidney disease, seizure disorders, mental illness, urination problems and alcohol or drug addictions. Codeine can be very harmful during and after the pregnancy and it may cause severe complications in a newborn. The effects of codeine can even be life-threatening in some cases.
Side Effects
Side effects of codeine generally affect the patients who suffer from renal and liver disease in a more severe way. Side effects of the nervous system include stupor, mental depression, delirium, somnolence, respiratory depression, dysphoria, increased risk of hip fractures and falls and in some cases even seizures may occur.
The most common cardiovascular side effects of codeine include dizziness and hypotension. Among the most frequent gastrointestinal side effects of codeine are vomiting, nausea and constipation, while some rare cases have also included acute pancreatitis and colonic perforation. Urinary retention is the most common genitourinary side effect of codeine. Dermatologic side effects commonly induced by codeine include dermatitis, scarlatiniform eruptions, increased histamine release and rashes.
Codeine can also sometimes trigger acute renal failure. It can also be associated with exercise-induced anaphylaxis in certain cases. Codeine can also sometimes be the main cause of the hypersensitivity syndrome. Intravenous administration of codeine can sometimes cause the pupil diameter to decrease significantly. Codeine withdrawal symptoms may include restlessness, tremor, agitation, vomiting, perspiration, abdominal cramps, insomnia and blurred vision.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...