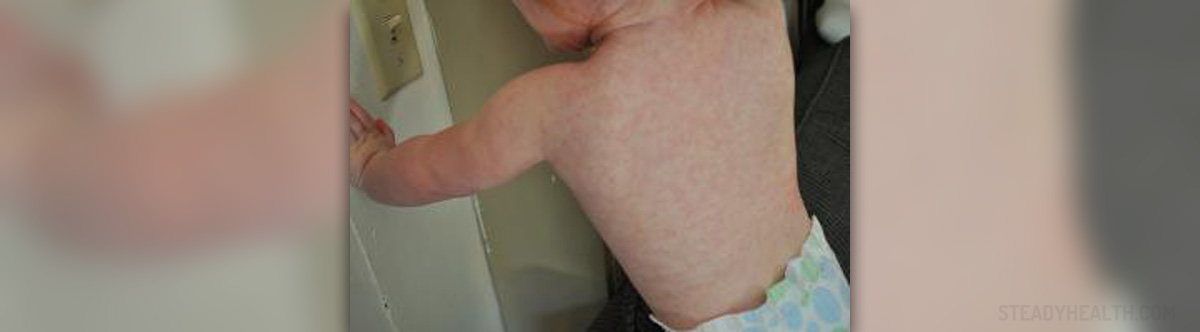
Roseola is a common infection that appears in thechildren under 2 years of age. The medical term for the roseola that occurs ininfants is roseola infantum. Rarely, itoccurs in adults. It is a generally mild infection and is not a seriouscondition.
Causes of roseola
This infection is caused by two strains of human herpesvirus, the strain six and seven. In the majority of cases, the human herpesvirus six is responsible for the occurrence of this viral infection. However,the both viruses are referred as roseolovirus.
Roseola is a very contagious condition. It can beeasily spread to the people who are around. For example, when an infected infantis coughing, the virus can (in droplets) pass to the person who is healthy. The herpesvirus is in the saliva or oral secretion and every contact with it can lead tothe development of roseola. The incubation period for the roseola is about tendays. It means that it is necessary to pass ten days from the virus exposure tothe appearance of the first symptoms in an infected person. Even during theincubation period, the roseola is contagious and the infected child isinfectious.
Symptoms of roseola
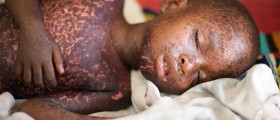
One of the most common symptoms of this viralinfection is the occurrence of a high fever. It usually lasts one to threedays. In severe cases, when the fever is extremely high, febrile seizure mayhappen. It is manifested through the loss of consciousness, incontinence and lossof control of the bowel. In addition to these symptoms, twitched face, arms orlegs may also appear. Another common symptom of roseola is the skin rashthat occurs once the fever subsides. This roseola skin rash usually affectsthe skin on the face, abdomen, neck and the back. However, it may also occurthat the whole body can be covered with the rash. Other symptoms of this infection are runny nose,cough and diarrhea, as well as nausea and vomiting. Furthermore, the infant mayhave swollen lymph nodes under the neck.
Treatment for roseola
Roseola is a viral infection that has the symptomsthat are the same as in many other viral infections. Therefore, it is verydifficult to diagnose this condition. However, a blood or urine test can showthe type of the infection. Once it is diagnosed, there are no specialtreatments, only in the case of high fever; antipyretics should be given to theinfected child in order to lower the body temperature. The child also shoulddrink plenty of water and stay well hydrated.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...