The Herpesviridae is a large family of herpes viruses that causes different diseases in animals, and humans. Herpes viruses got their name from the Greek word herpein, which literally translates as “to creep.” The word reflects the nature of the infections caused by herpes viruses, which are typically latent and often recurring. In colloquial use, herpes virus usually refers to the herpes simplex virus, which is only a subtype of herpesviridae family. Medically speaking, herpesvirus is a virus of the taxonomic family herpesviridae. There are eight different types of herpes viruses.
Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2
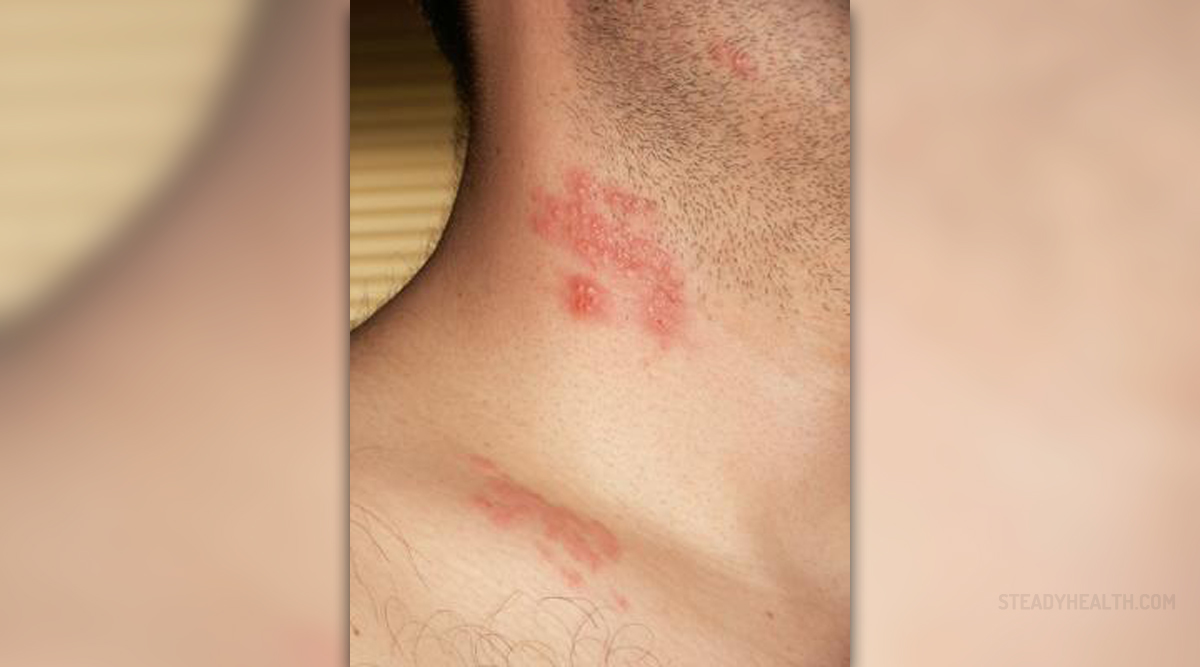
These are actually two viruses of the herpes virus family, also known as HSV-1 and HSV-2. Herpes simplex virus 1 is responsible for most cases of cold sores in humans. Herpes simplex virus 2 usually causes genital herpes. The symptoms of herpes simplex infection include watery blisters forming in the skin or mucous membranes of the lips and genitals. Virus is generally spread from contact with an infectious area of the skin during reactivations of the virus.
Human herpesvirus type 3
This type is also known as varicella zoster virus. It is mostly responsible for chicken pox in children and shingles in adults. Other known names for herpesvirus type 3 are chickenpox virus, varicella virus, zoster virus, and human herpes virus type 3 (HHV-3).Human herpesvirus type 4
This species of herpesviridae is also known as Epstein-Barr virus. It causes infectious mononucleosis in humans, and it is one of the most common viruses in humans. Most of the infected individuals have adaptive immunity to this virus, and about 90–95% of adults in the United States have evidence of previous infection.
Human herpesvirus type 5
This species is also known as Cytomegalovirus, or CMV. Infections with Cytomegalovirus are typically associated with problems in salivary glands. The infection is usually unnoticed in healthy individuals, but it may be severe and even life threatening for immuno-compromised patients.
Human herpesvirus type 6
Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) inhabits the bodies of almost 100% of the human population all over the world. It generally causes common childhood diseases, such as roseola infantum. The prevalence of the virus in the body increases with age.
Human herpesvirus type 7
Similarly to HHV-6, Human herpesvirus type 7 usually causes skin conditions in infants and sometimes manifests with other associated symptoms such as acute febrile respiratory disease, fever, rash, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Human herpesvirus type 8
This type also known as Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. It commonly occurs in AIDS patients and seems to have a significant role in cancer development.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...