What are Moles?
Moles — or nevi — are skin growths made up of highly pigmented skin cells. Most are completely benign, and almost everyone has between 10 and 40 moles on their body. Due to increased awareness of skin cancer, however, increasing numbers of people will panic when they see a new mole, or notice that a mole has changed.
It is wise to seek medical attention when you have a mole or multiple moles, that:
- Are asymmetrical in shape, with one half looking very different from the other.
- Have irregular borders; rather than having a defined, neat, ending, these moles may have blotchy or jagged edges.
- Contain multiple colors or change color over time.
- Grow larger over time, change shape, or become more raised.
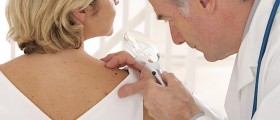
When you go to the doctor about a concerning mole, they may be able to tell whether it is potentially malign or otherwise problematic with a physical examination. Your doctor may also wish to take a biopsy to be tested in a lab. In some cases, after the results come back, they will recommend that you have the mole removed.
What Do you Need to Know About Mole Removal?
Cancerous moles, such as malignant melanoma, always need to be removed as soon as possible, and your doctor will also advise you to have a mole with atypical features — which indicates that it could become malignant in the future — removed. In addition, you may elect to have an otherwise harmless mole removed if you tend to cut it while shaving, or if it is in an area that is constantly exposed to friction.
Mole removal is a simple and routine surgical procedure that is carried out on an outpatient basis — meaning that you can go home shortly after the mole is excised. After giving you a local anesthetic, your doctor will be ready to get to work without causing you any pain. They will remove your mole in one of three ways:
- A shave biopsy means that your mole is removed with a very sharp razor blade. Some of the surrounding skin will also be excised.
- In a punch biopsy, your doctor — most likely a dermatologist — will use a special tool that essentially acts as a hole punch, but for moles.
- A scalpel removal is the most traditional approach to mole removal. Like in any other surgery, your doctor will use a scalpel to cut out the mole and surrounding skin (to ensure all cells relating to the growth are gone). This type of mole removal leaves a larger wound and will require sutures.
- Mole (congenital melanocytic nevus) is one of the common lesions affecting the perception of facial aesthetics. Along with the size, shape and colour of the mole, even the position of a mole is a deciding factor with regard to facial beauty. A small mole just above the angle of mouth on the upper lip is said to be the perfect beauty spot. However, the same spot on the tip of nose may become an eyesore.
- Individuals are keen on removal of these mole/nevi for various reasons. Poor aesthetic appearance remains the main reason behind seeking a mole removal. Some nevi may need to be excised and biopsied if they clinically show features of malignant conversion. Apart from this, there are many patients who live with unaesthetic bothersome lesions, unaware of the fact that scar-free or minimal scar treatment modalities are available.
- There are various methods of treating benign lesions using surgical excision, electrosurgery, lasers, dermatome shaving, curettage, dermabrasion, chemical peels, ablative lasers, pigment-specific lasers, liquid nitrogen (cryotherapy) and no treatment (observation). The location of the nevus cell clusters also dictates the treatment modality for their removal.
- It is generally accepted that all nevi should be submitted for histological examination for medicolegal reasons. In a recent study, 2.3% of clinically diagnosed benign nevi were microscopically diagnosed as malignant tumours, either melanomas or basal or squamous cell carcinomas.
- Forty-five clinically confirmed cases of benign nevus were included in the study and randomly divided into three groups according to the technique used for excision, i.e. Group A - surgical excision, Group B - diode laser and Group C - electrosurgery. Post-operative wound evaluation was done using Stony Brook scar evaluation scale on post-operative photographs taken on days 7, 21 and 90 (3 months).
- Statistically, there was no significant difference between the three techniques on post-operative day 90. Clinically, hypopigmentation was noted with diode laser and electrosurgical excision of benign nevus.
What Happens After Mole Removal?
Patients will be instructed to keep the incision, which will be bandaged, clean, and dry for 24 hours — which means that no, you should not wash it. After that time is up, you can remove the bandage and gently clean it. You then need to pat the area dry with a clean towel, and apply antibiotic ointment to help prevent infection.
As your skin heals, avoid shaving the area where the mole was removed. If you receive any stitches, do not engage in physical activity that could cause them to come loose. Further, as your doctor will tell you, it is important to avoid medications that can increase bleeding, such as aspirin. Once your skin begins to heal, you may choose to apply a vitamin E cream to help prevent scarring — but depending on the mole removal method and the size of the mole, you may still have a small scar.
If the mole you had removed was suspicious, a biopsy will be carried out after the removal. You should receive your results in one to two weeks, and if you need to take further steps, your dermatologist will let you know at that time.
- medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000918.htm
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/moles/
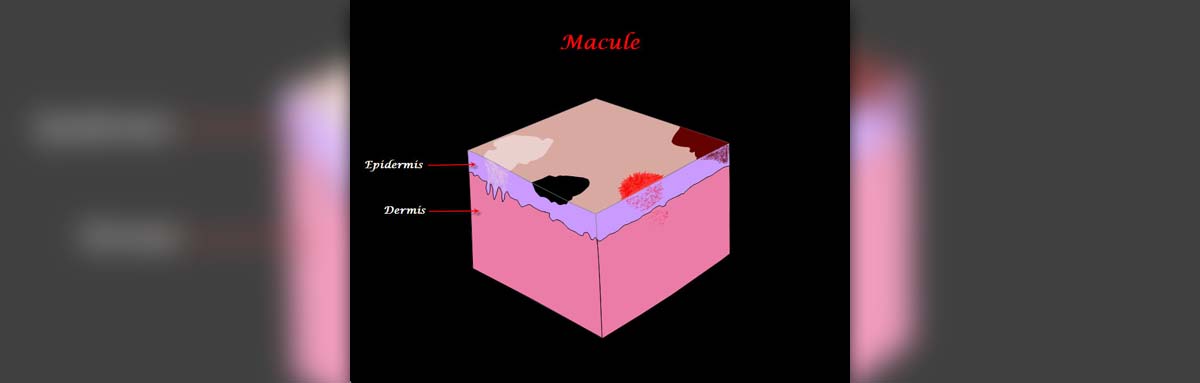
- Photo courtesy of AMH Sheikh by Wikimedia Commons: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Macule.jpg












Your thoughts on this
Loading...