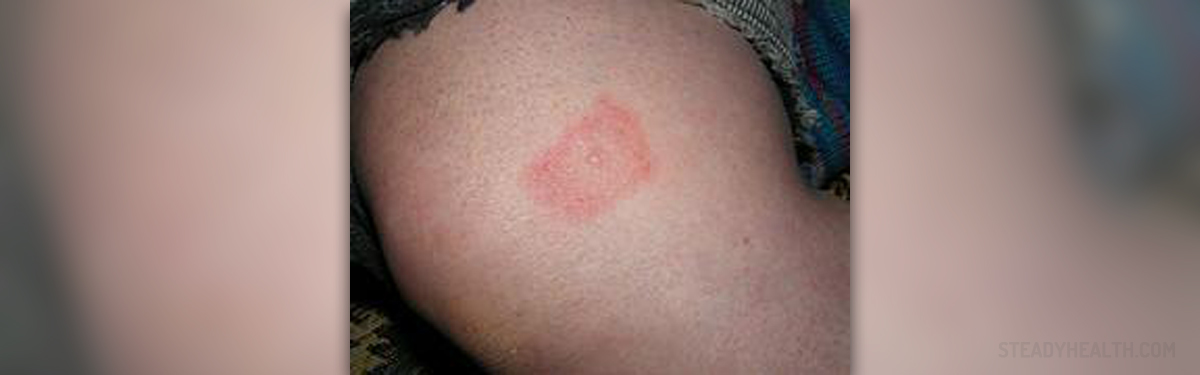
Leptospirosis is a bacterial infection that is spread from animals to humans. This rare, contagious disease, is caused by exposure to Leptospira bacteria. Common carriers of the disease are different animals such as rats, skunks, opossums, raccoons and foxes. In humans, the infection occurs through direct contact with the urine of an infected animal or soil and water contaminated with animal urine. A person may contract leptospirosis by ingesting the infected water or exposing unhealed breaks in the skin or mucus membranes to contaminated soil, water or animal urine.
Leptospirosis is common for tropical climates in which it occurs throughout the year whilst in other areas the disease is seasonal. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 100-200 new cases are reported each year in the United States with the highest number of leptospirosis cases occuring in Hawaii.
Signs and Symptoms of Leptospirosis
The incubation period for leptospirosis is 2 to 25 days. Initially, the disease causes flu-like symptoms such as headaches, muscle aches, fever and chills, dry cough, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Red and watery eyes and eye pain associated with bright lights are common too. This is the first phase of leptospirosis in which the symptoms improve after fifth to ninth day.
This is followed by the second phase in which the symptoms like stiff neck and high fever return. In some cases meningitis characterized by inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord (meninges) may occur as well. Leptospirosis at this stage may be also accompanied by abdominal pain, skin rash, sore throat, bone and joint pain and swollen lymph glands. Some patients additionally develop liver, lung, kidney and heart problems. The severe form of leptospirosis is known as Weil’s syndrome and is featured by liver and kidney failure. Prevention of Leptospirosis
Increased risk of leptospirosis have farmers, veterinarians, ranchers and sewer workers as well as people who engage in recreational activities such as swimming, canoeing, hiking and rafting in potentially infested areas. To lower the chances of contracting leptospirosis such individuals should take doxycycline or amoxicillin until the exposure ends. People at occupational risk should wear protective clothing and footwear. Stagnant waters in warmer areas should be always avoided.
Vaccination against leptospirosis exists, but is not available in the United States. However, it is used in some countries in Europe and Asia and is given yearly like an influenza vaccine. In Cuba, scientists are trying to develop long-acting vaccine against the disease.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...