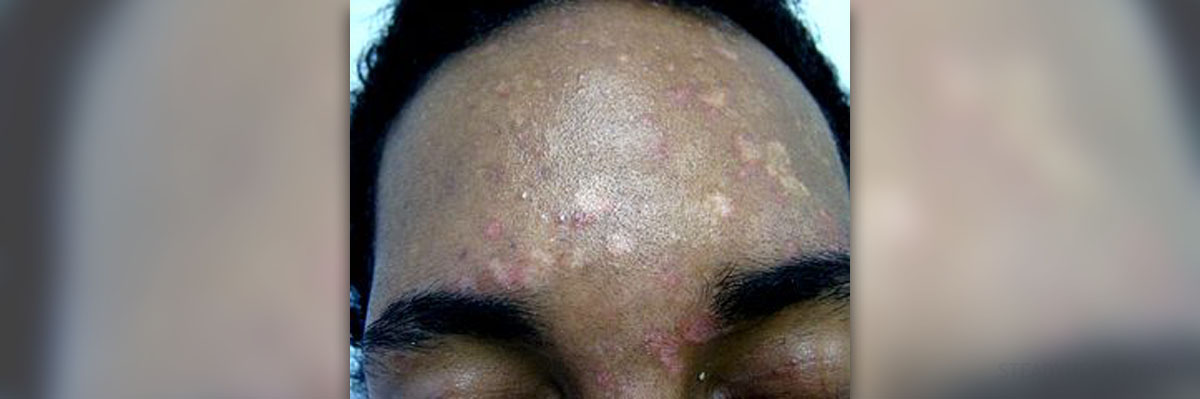
Clinical Characteristics of Tinea Versicolor
This skin condition develops as a consequence of the presence of certain fungi on the skin. Namely, they form a tissue-thin coating and are responsible for uneven appearance of the skin.
The skin of an affected individual is covered with small and scaly patches. They contribute to visible skin discoloration. Once they are formed, patches tend to grow in time and become bigger. They may even merge. Such patches become more prominent after sun exposure and may cause mild itching. The actual color of skin patches varies and may be white, red, tan or dark brown. The combination of the previous is also possible. Tinea versicolor equally affects all races.
Even though tinea versicolor may occur on any part of the skin, there are certain parts of the body particularly susceptible to the condition. They include the back, neck, chest and upper arms.
How to Prevent Tinea Versicolor?
Some believe that this skin condition may be prevented if one abstains from applying oil or oily products to the skin. Wearing tight, restrictive clothes or clothes made from synthetic fiber may also contribute to the disease, thus needs to be avoided as well. Once the problem has developed, by reducing exposure to sunlight one may prevent further spread of skin patches.
Prevention of recurrent tinea versicolor is achieved with topical or oral treatments such as application of selenium sulfide lotion (every 2-3 weeks), intake of ketoconazole tablets (once a month) and itraconazole capsules (also once a month).
Treatment for Tinea Versicolor
The condition may respond well to over-the-counter antifungal drugs (selenium sulfide shampoo, miconazole, clotrimazole, terbinafine etc.). However, if this is not the case one may be prescribed more potent topical or oral medications. Selenium sulfide 2.5% lotion, Ciclopirox (cream, lotion or gel) as well as ketoconazole (cream and shampoo) are applied directly to the affected skin. On the other hand, ketoconazole tablets, itraconazole capsules and fluconazole tablets are taken orally. The treatment is usually successful. However, the skin discoloration may linger for several weeks or sometimes up to a few months. Warm and humid weather aggravates the skin changes.
- medlineplus.gov/tineainfections.html
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/pityriasis-versicolor/
- Photo courtesy of Grook Da Oger by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pityriasis_versicolor_frontal_retouche.jpg













Your thoughts on this
Loading...