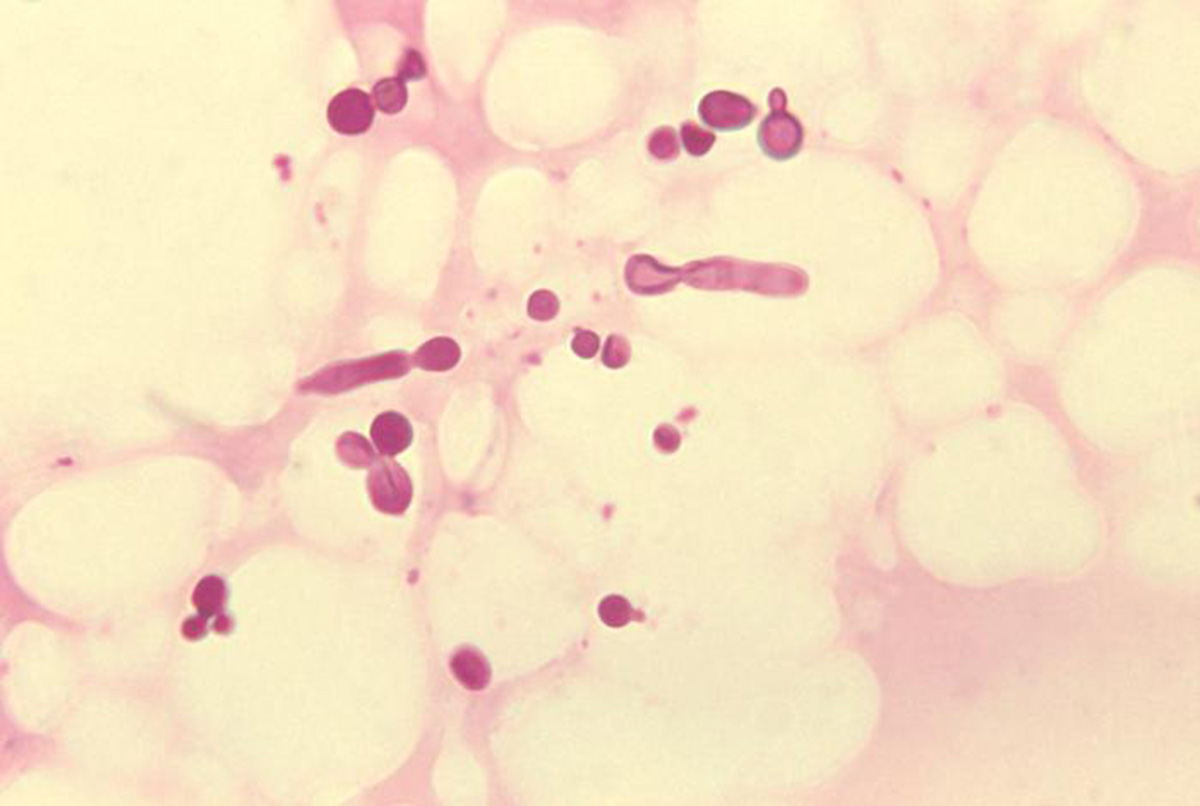
Tinea versicolor is a skin condition characterized by a rash on a trunk and on proximal extremities. Tinea versicolor is also known as dermatomycosis furfuracea, pityriasis versicolor and tinea flava. This condition is caused by yeasts, that normally live on human skin but under certain conditions overgrow causing medical troubles. Fungi grow and thieve in dark and moist surfaces, and when it is hot and humid they tend to grow more quickly. Tinea versicolor is most commonly caused by Malassezia globosa, even though Malassezia furfur causes a small number of cases.
Symptoms of tinea versicolor
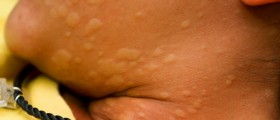
Tinea versicolor is characterized by small patches on the skin, which seem to be lighter than the rest of the skin surface. The patches usually appear on oily areas of the body such as the chest, back, shoulders, and upper arms.
In some cases, patches can appear darker than the skin, or pink in color. Generally, there will be a noticeable difference between the normal and affected surfaces. The color of the patches actually depends on the normal skin color. In people with dark skin tones the loss of color is common, while patients with lighter tan may experience the increase in the skin color.
The fungus will prevent the skin from tanning and pale spots may drastically stand out as the skin tans.
The patches are irregularly shaped and about 0.6 to 2.5 cm in diameter. It is not unusual to see that the patches are merging together to form a larger patch.
The patches may appear dry and often scaly. The scale is usually ash-like and accompanied with intensive itching. The itching is more pronounced after vigorous physical exercise or after being in a hot or warm environment.
Epidemiology
It is estimated that tinea versicolor affects somewhere between 2 and 8 percent of the United States population. However, the exact incidence may be even higher, as many people do not seek medical help for this benign condition. This condition affects people all over the world, and it is most frequent in hot and humid parts of the world. The disease usually affects younger people, aged between 15 and 24. The explanation behind this fact is that the sebaceous glands of young people are more active and this fungus actually affects the oily areas of the body.
Treatment
Treatment for tinea versicolor is relatively simple. There are many over-the-counter medications that are commonly used twice a day for 10-14 days. Various antifungal creams can also be applied topically. The important thing to remember is that the tinea versicolor rash tends to linger even after the successful treatment. This often leads people to think that the condition is still present.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...