The skin contains many cells including melanocytes, pigment cells located in the surface layer of the skin. These cells synthesize melanin, a pigment of the skin and mucous membranes. Melanin is essential because it protects the skin from harmful UV rays. Depending on the amount of melanin present in the skin, people have different skin color.
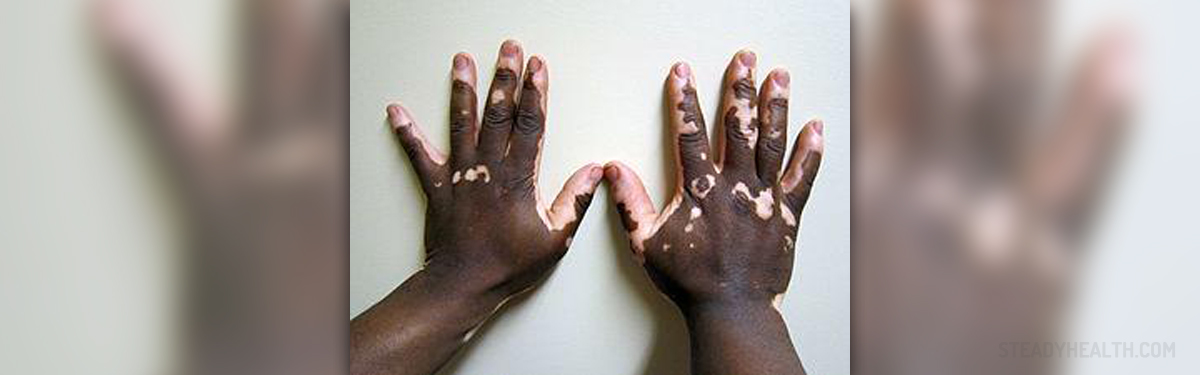
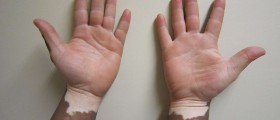
Vitiligo is a skin disorder characterized by skin depigmentation due to lack of melanin. The condition usually starts between the age of 20 and 30. Different parts of the skin are affected including the face, neck, armpits, groins, hands and knees. Sometimes depigmentation is in a form of small patches affecting the entire body. After initial skin depigmentation, the disorder stays stagnant. Depigmentation episodes can also reoccur.
Vitiligo Causes and Risk Factors
Even though the exact cause of vitiligo remains unknown, most experts believe that a combination of many factors contribute to the onset of the disease. Some of these factors are heredity, exposure to certain chemicals (phenol, catechol etc.), emotional/physical stress, autotoxic response, skin injuries, burns and inflammatory skin disorders. The condition may also be autoimmune in origin although the presence of autoantibodies has not been confirmed yet.
It is also possible to develop vitiligo if one is already suffering from some medical conditions like diabetes, pernicious anemia, thyroid gland disorders, Addison's disease, uveitis and alopecia areata.
Prevention of Vitiligo
Vitiligo is not contagious and cannot be transmitted from one person to another. As far as prevention of the condition is concerned, any skin patch should be thoroughly examined. One should maintain good health and keep the immune system strong.
Furthermore, it is essential to avoid application of any unproven topical medication on the skin, especially corticosteroids. Some say that even avoiding excess consumption of sour things can help.
Treatment for Vitiligo
The goal of any treatment for vitiligo is improvement of the skin's appearance.
Medicamentous treatment includes topical steroid creams, psoralen photochemotherapy (topical psoralen photochemotherapy or oral psoralen photochemotherapy) and depigmentation.
Surgical treatments for vitiligo are autologous skin grafting, skin grafts using blisters, micropigmentation (tattooing) and autologous melanocyte transplants.
Patients are due to minimize sun exposure and always use sunscreen because sun can increase contrast between the healthy and affected skin. Many patients may opt for different cosmetic products which can camouflage skin depigmentation and make the skin tone look even.
Finally, for all individuals suffering from vitiligo who simple cannot face their illness it is best to consult mental health professionals or to attend a vitiligo support group.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...