What is nephrolithiasis?
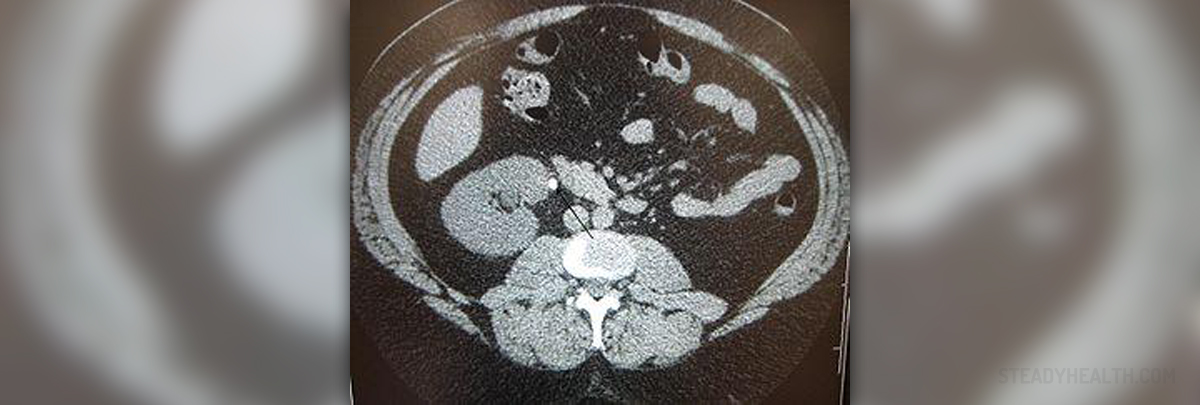
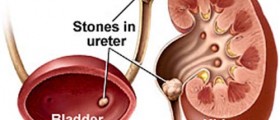
Nephrolithiasis is a condition characterized by the formation of calculi in the urinary tract. The calculi, or stones, can be formed in the kidneys, called renal calculi, or in the ureter, called ureteral calculi.
Nephrolithiasis or urinary tract stone disease, as it is also called, has been known for millennia, in fact, kidney stones have even been found in the Egyptian mummies. It is a fairly common disease that, unfortunately, causes a lot of pain. Renal colic, which is a name given to the pain experienced due to calculi, is often compared to childbirth, gunshot wound, burns of broken bones.
Renal colic can be managed in different ways. One way is to let the stone pass by itself through urination, but if it is too large, it may have to be broken down into smaller pieces that can pass the urinary tract. However, the calculi tend to reoccur. Therefore, it is the task of every medical professional, whether it is family practice, specialist, emergency room attending or a nurse, to provide the patient with the information about preventive measures. This is not only directed towards sparing the patient the excrutiating pain due to calculi, but also towards preventing some of the serious complications that may arise from nephrolithiasis.
Prevention of nephrolithiasis
Since renal and ureteral calculi often result from high levels of uric acid in urine, it is necessary for people who have already suffered from renal colic to have those levels checked on regular basis. Excessive uric acid can be managed with oral medications such as allopurinol and potassium citrate. Reducing the intake of foods rich in animal protein, such as meat, should also be reduced. Calculi caused by calcium accumulation can be prevented by reducing the intake of calcium-rich foods, while those who have oxalate stones should avoid tea, chocolate and spinach.
It is also believed that regular consumption of cranberry juice can be very effective as prevention of nephrolithiasis. It is also recommended to drink ample amounts of plain, filtered water. The recommended amount ranges from 1.5 liter to 2.5 liters every day. The more water is consumed, the less chance one has of developing kidney or ureter stones.
Diet high in potassium and magnesium is believed to reduce the chance of developing renal or ureteral stones. Beverages such as cola and grapefruit juice should be avoided. Sodium intake or salty foods should be limited, if not avoided. Low-sodium diet is beneficial for other conditions and health problems as well, not just for nephrolithiasis.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...