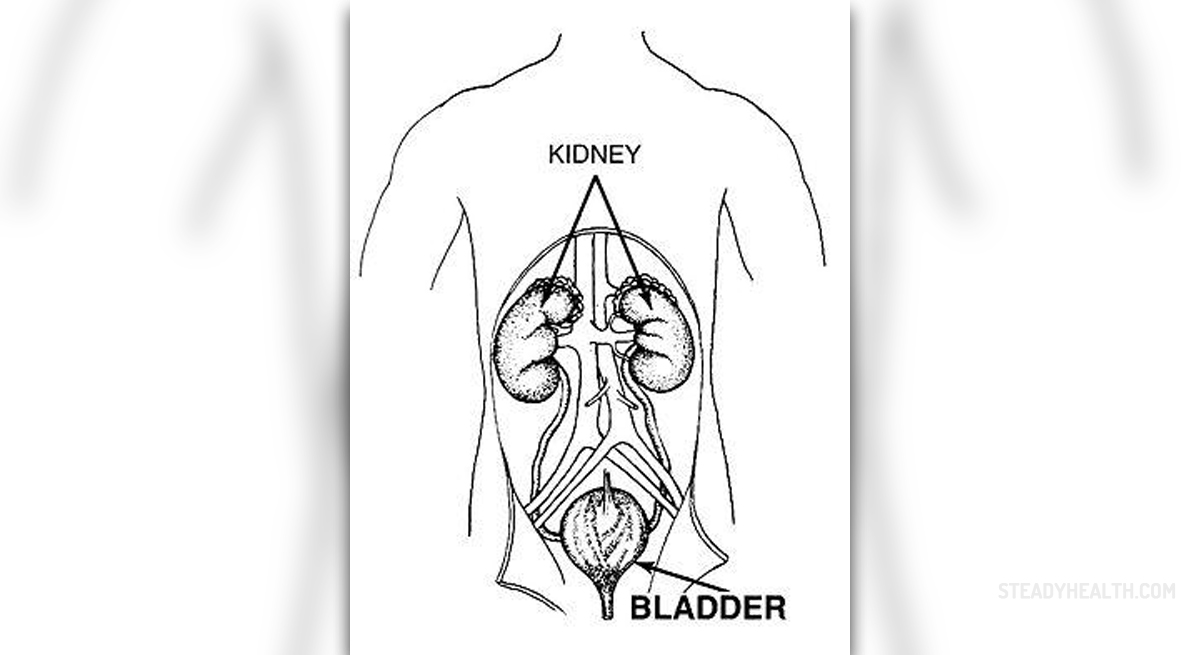
What Is Urinary Tract Obstruction?
Urinary obstruction may occur in any part of the urinarytract, but there are still certain points and organs which are more susceptibleto obstructions than others. There are three critical points and those includethe UVJ, the crossing of the ureter over the area of the pelvic brim at thelevel of the iliac vessels, and the UPJ. Urinary tract obstruction is arelatively common medical problem which may also be associated with certainmedical complications such as urinary tract infections, painful sensations,loss in renal function, sepsis and sometimes even death. Those who suspect theyhave urinary tract obstructions should pay a visit to an urologist. There arecertain types of urological emergencies which require immediate medicalattention and treatment and those include nausea and vomiting sufficient tocause dehydration, uncontrolled pain, any suspicion of neurologicaldysfunction, renal failure, obstruction accompanied by infections or fever, anytype of obstruction in a solitary kidney or complete urinary tract obstruction.
Diagnostic Procedures
There are a number of diagnostic procedures which need to beperformed in patients who suspect they suffer from urinary obstructions. Amongsuch procedures, the most common ones include several types of laboratory studieswhich include complete blood cell count, basic metabolic panel and urinalysis.The complete blood cell count may show anemia which indicates malignancy, chronicrenal insufficiency or blood loss. Some cases may involve leukocytosis which isan excellent indicator of infections. Basic metabolic panel is an excellent wayof diagnosing renal insufficiency by showing the levels of creatinine. Somecases of renal insufficiency may also be held responsible for the onset ofacidosis or hyperkalemia. Urinalysis is an excellent way of evaluating thepresence of hematuria or different sorts of infections. It may also show ifthere are any inflammatory conditions present in urinary tract. If it shows thepresence of RBCs in the urine it may be an indication of tumors of stones insome cases. Other diagnostic procedures include cystoscopy and cystoscopy withretrograde pyelography. Cystoscopy involves passing a microscopic camerathrough the urethral meatus all the way into the bladder in order to check forany abnormalities in the bladder, bladder neck, prostatic urethra and theurethra. Retrograde pyelography sometimes accompanies the aforementionedprocess of cystoscopy and it involves the injection of radiographic dye intoureteral orifices. Further on, the process called fluoroscopy is then used forthe visualization of any defects or abnormalities.
How Is this Condition Treated?
Generally speaking, all cases acute retention need to betreated by utilizing the process of urinary catheterization. If a personsuffers from mild symptoms which do not affect the quality of life and do notinvolve any further complications, he or she simply needs to reduce the intakeof fluids and avoid drinking alcoholic and caffeinated beverages. Alphablockers and 5 alpha reductase inhibitors are often used as medicaments. Allthose who suffer from acute upper urinary tract obstruction need to be wellaware of the fact that most stones that are smaller than 5 millimeters indiameter will pass on their own. It is usually in cases of stones that arebigger than 10 millimeters in diameter that an intervention is required. Thesymptoms of such acute cases of urinary obstruction in most cases do not lastlonger than 72 hours. A person usually suffers from painful sensations,inflammatory conditions and vomiting which can be managed quite easily bytaking diclofenac or morphine. Those with renal colic should not worry much aslong as they ingest sufficient amounts of fluids. Alpha blockers as a means ofmedical expulsive therapy may sometimes be used in order to increase the chanceof passing a stone. Some cases of larger stones may also need to be taken careof by utilizing extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. If an urologistdetermines that the urinary obstruction is accompanied by an infection,drainage needs to be established as soon as possible, mostly by inserting apercutaneous needle right above the obstruction. This process is medicinallyreferred to as nephrostomy. In cases of pelvi urereric junction obstructionsthere are also a few treatment options which can be used. They includeureteroscopic endoureterotomy, endopyelotomy and pyeloplasty. Ureteroscopicendoureterotomy is used in cases accompanied by ureteric strictures, endopyelotomyinvolves an incision through the stenosis while the pyeloplasty requires anassistance from a robot. Malignant obstructions are commonly accompanied byunderlying conditions which need to be treated with percutaneous nephrostomy orureteric stenting so that the obstruction can be relieved. In cases of idiopathic retroperitonealfibrosis there needs to be a placement of stent or an ureterolysis needs to beperformed so that the obstruction can be relieved. In most cases certain types ofimmunosuppressive medicaments and corticosteroids are used as a part of thetreatment method. Malignancy needs to be excluded by performing a biopsy ofperi aortic mass.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...