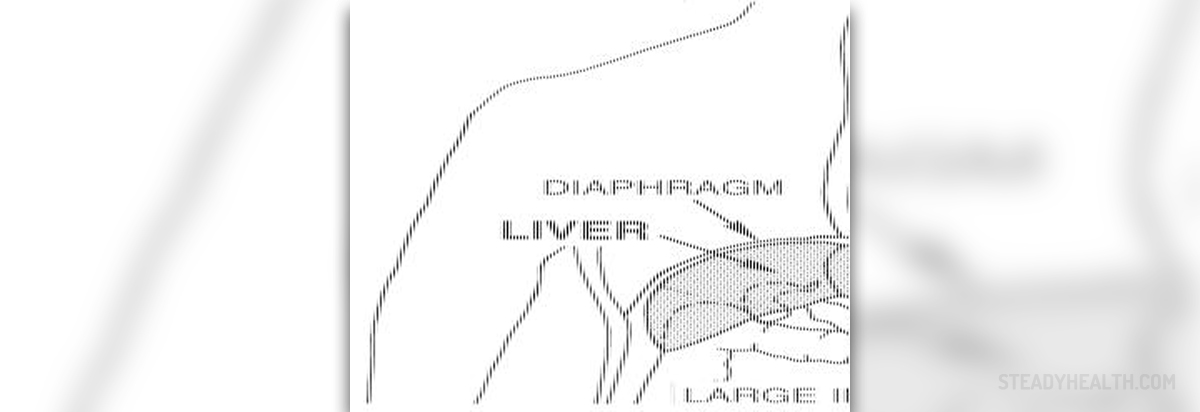
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Depending on the cause of the inflammation, doctors refer to it as viral, medications and toxic-induced hepatitis. Viral hepatitis, on the other hand is classified according to duration of infection either as acute (has short course) or chronic hepatitis (lasts for a long period of time).
Symptoms of hepatitis may be mild, such as fever, muscle and joint aches, nausea, vomiting, poor appetite, fatigue and diarrhea. In some other cases, patients may have problems such as jaundice, lightly colored stool but dark urine, some itching, dizziness, drowsiness, headaches or even circulation problems, hives or enlarged spleen.
Viral Hepatitis
Current medicine knows several types of viral hepatitis, called hepatitis: A, B, C, D and E, as they were caused by hepatitis viruses A, B, C, D and E. Hepatitis A or infectious hepatitis can be spread from infected person to another or by eating contaminated food or water or through cooking utensils. This infection of the liver is an acute problem.
Hepatitis B Or serum hepatitis is the most serious of all these conditions and it spreads through sexual intercourse or exposure to infected blood via transfusion, open sores, cuts, sharing razors or from a mother to a child at delivery. Hepatitis B is usually acute but some 10% of all patients have chronic form of this disease and may develop liver cirrhosis, failure or even liver cancer.
Hepatitis C is spread only via blood transfusions or contaminated needles, rarely via sexual contact or from a mom to her child at birth. Chronic hepatitis C may cause liver cirrhosis.
Hepatitis D is common for intravenous drug addicts already suffering from hepatitis B, while hepatitis E is common in the area around the Indian Ocean.Non-Viral Hepatitis
Alcoholic and drug-induced hepatitis are two main types of non-viral hepatitis. There are also additional types of hepatitis caused by some autoimmune problem (autoimmune hepatitis) or abnormal collection of white blood cells in the liver (known as granulomatous hepatitis).
How to Prevent Hepatitis?
Hepatitis A is easily prevented if you remember to eat only freshly cooked food and drink commercially bottled water and wash your hands after using the toilet. Additionally, there is vaccine against this hepatitis. Hepatitis E can be prevented in the same way as hepatitis A.
Safe sex and avoidance to share needles, razors or toothbrushes is the best way to prevent hepatitis B. Make sure to tell your sexual partners if you are carrier of this virus. Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for people in high risk groups. All mentioned measures will also prevent hepatitis D.
Hepatitis C prevention also requires practicing safe sex, limitation of alcohol intake, avoidance of sharing personal toiletries or IV needles.
Limit amount of alcohol you drink and you shouldn’t have problems with alcoholic hepatitis. Always be aware of the chemicals you use, face the sprays away from your body and if you can wear protection.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...