
Our livers perform many critical functions and any damage that occurs to the liver can have serious consequences for our bodies. Among its many functions, the liver produces and stores bile. This substance helps us to digest food. The liver is located in the upper right section of the abdomen, and is given protection by the rib cage. Each liver cell has two sources of blood - the hepatic artery supplies oxygen rich blood, and the portal vein transports nutrients from the intestine and spleen. The portal vein brings chemicals from the digestive tract to the liver in order to detoxify and filter them.
Causes
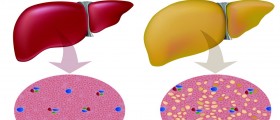
The liver can be damaged by several means. Hepatitis can cause an inflammation of the liver cells, cholestasis can obstruct the flow of bile, steatosis can lead to an accumulation of cholesterol or triglycerides. In addition to these conditions, damage can occur if blood flow is interrupted, or if chemicals and minerals infiltrate the liver tissue. Alcohol abuse is another major contributor to the onset of liver disease. Alcohol is a toxin, and it has a particularly negative effect on the liver cells. Alcohol abuse can lead to steatosis and cirrhosis, a scarring of the liver that causes the liver cells to lose function.Medications
Certain medications or drugs can also lead to liver disease. Excess amounts of Tylenol, Panadol, Vicodin, Lortab and Norco can all cause permanent liver failure. Statin medications - used to control cholesterol - can cause liver damage even when taken in the prescribed doses. Usually, when you stop using statin medication, the liver will return to its normal function. Niacin, nitrofurantoin, amoxicillin, clavulanic acid, tetracycline, isoniazid can all lead to problems with the liver. When using these drugs, stick to the recommended dosage. As with statin medications, liver function will usually return to normal upon cessation of intake.
An overdose of herbal medicines or supplements containing vitamin A, kava kava, ma-huang and comfrey can also potentially cause liver problems. The consumption of certain types of wild mushrooms should also be avoided, as many of these mushrooms can be poisonous to the liver.Hepatitis and other causes
Infectious hepatitis is a major cause of liver disease. Hepatitis is a group of virally transmitted diseases, which in some forms can be spread through means such as oral or fecal transmission. These diseases are known as Hepatitis A, B, C, D and E. Normally, hepatitis is spread through the exchange of bodily fluids. Hepatitis can also be spread through the use of contaminated needles, contaminated blood and sexual contact. Mononucleosis, adenovirus and cytomegalovirus are other types of virus that can affect the liver. In addition this, hemochromatosis, Wilson’s Disease and Rocky Mountain disease (viral) are other potential causes of liver problems.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...