
Asthma can be a major irritation and, at times, a serious problem. Some people experience the condition in moderate doses, while for others, it can interfere greatly in their everyday lives. Sufferers are also at risk of a potentially fatal asthma attack. Unfortunately, asthma cannot be cured, merely controlled. Treatment is usually symptomatic and generally involves avoidance of triggers and use of an inhaler designed to control the symptoms. Causes
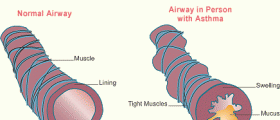
The condition itself narrows and swells the body’s airways. This can cause breathing problems and a production of excess mucus, all of which generally manifests outwardly as shortness of breath, coughing and wheezing. The condition normally develops as a result of genetic and environmental influence. Triggers and causes vary between individuals, but normally these triggers take similar forms. For example, physical activity, colds, air pollutants, pollen, mold, dust mites are all common triggers of asthma.
Other factors can also lead to an onset of the condition: allergic reactions to food, sulfites in food and drink, certain medications and major stress are all potential triggers. For women, the menstrual cycle can also cause asthma.Living with asthma
As indicated, asthma can be controlled. Your doctor will give you a plan that will help you to come to terms with the condition and avoid further problems. You will be instructed on how to deal with an asthma attack, and also told which medications and precautions should be taken when dealing with the condition.
Try to identify what causes the onset of asthma. When you do, minimise contact with these triggers, which can include outdoor irritants like pollen and cold air. Make sure you are in control or at least aware of your breathing. Identify the warning signs of an asthma attack. These signs will include shortness of breath, wheezing and coughing. Further to this, use a home peak flow meter to measure your airflow through the lungs, as this can be a good early warning system.
Ensure that you address the attacks as soon as they occur. The quicker you act, the less serious it will be. If you are measuring your peak flow correctly, you will get some indication of the onset of an attack. In this case, cease any activity that may trigger an attack. In addition to this, take your medication in the correct dosage and at the right times. Even if you see an improvement, don’t change your course of medication without consulting a doctor. Also, don’t overuse your inhaler. Over-reliance on inhalers is generally not ideal and usage should be moderated.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...