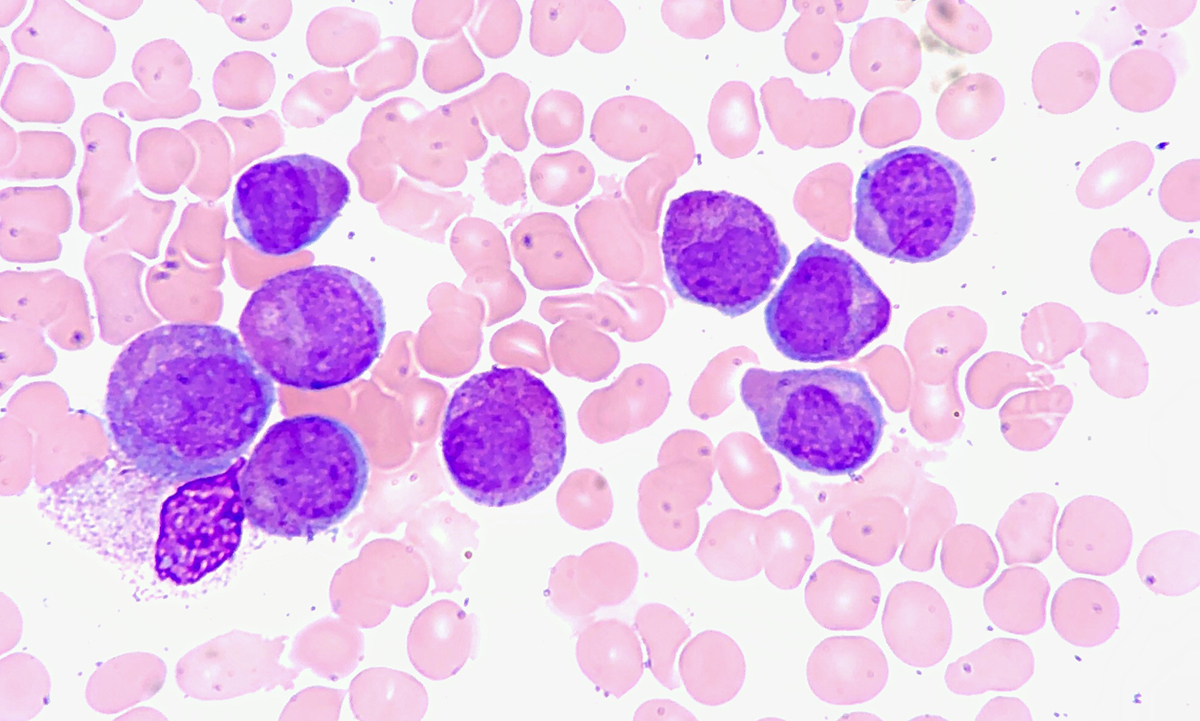
Pancytopenia is a medical condition which features with insufficient number of all three types of blood cells. Pancytopenia includes reduction in red blood cells (anemia), reduction in white blood cells (leukopenia) and low platelet count. This is why symptoms of pancytopenia actualy represent combination of symptoms characteristic from anemia, leukopenia and thrombocytopenia. In some people there are only abnormalities of two types of blood cells and this condition is known as bicytopenia.
Causes of Pancytopenia
A variety of medical conditions may cause pancytopenia. Any problem which leads to improper functioning of bone marrow and inadequate production of blood cells may lead to pancytopenia. Many patients who have developed pancytopenia were previously suffering either from anemia, leukopenia or from thrombocytopenia.
Apart from bone marrow diseases other illnesses which may contribute to occurrence of pancytopenia include aplastic anemia, dyceratosis congenita, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, leukemia, leishmaniasis, malignant osteoporosis, severe viral infections, HIV, hypersplenism, and many more.
Pancytopenia may also occur due to poisoning such as arsenic poisoning. Furthermore, pancytopenia may be induced by certain medications. Those include antibiotics, cytotoxics, anti thyroid medications, non steroid anti-inflammatory drugs and some medications for heart conditions and elevated blood pressure.
Symptoms of Pancytopenia
There is a mixture of symptoms of anemia, leukopenia and thrombocytopenia.
Insufficient amount of red blood cells leads to pallor, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, rapid heart rate and shortness of breath. Inadequate coagulation of blood cause prolonged bleeding even after small injuries. This is why patients suffering from pancytopenia commonly experience bruising and bleeding from the nose and gums. Women may suffer from excessive menstrual bleeding while both genders may also develop petechiae which are reddish spots on the skin caused by mild bleeding from the skin blood vessels. Insufficient amount of white blood cells causes frequent infections.
Treatment for Pancytopenia
It is essential to find the underlying cause of pancytopenia and to start with supportive care as soon as possible. Anemia is treated with blood transfusions of packed red cells. It is important to maintain the appropriate level of hemoglobin. Blood is given carefully so that circulatory overload can be avoided. Patients who are thrombocytopenic must not be given intramuscular injections and are not supposed to brush teeth. If there is active bleeding it is brought under control with infusion of platelet concentrates. Special attention is paid on prevention of infection. Maintenance of skin hygiene, excellent dental care and rectal hygiene are of great importance. Some patients may be given antibiotics prophylactically. Majority of patients are hospitalized until the symptoms are brought under control.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...