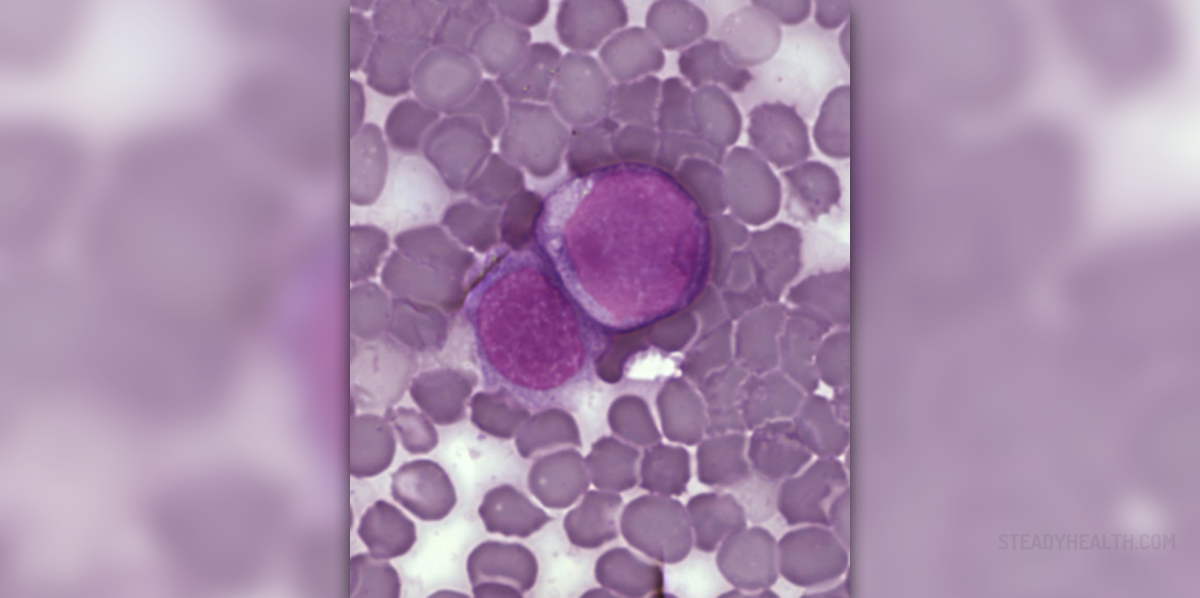
Acute Myeloid Leukemia - Overview
Acute myeloid leukemia (acute myelogenous leukemia) is a cancer made of myeloid line of blood cells. These cells grow quickly, multiply uncontrollably and accumulate in the bone marrow. They are found in the bone marrow and interfere in normal production of all blood cells. Acute myeloid leukemia is the most common type of acute leukemia in adults. The number of new cases increases with age.
The symptoms of acute myeloid leukemia develop as a consequence of replacement of bone marrow cells with abnormal cancer cells.
The actual cause of acute myeloid leukemia remains unknown. There are several factors associated with the onset of the disease. The conditions is highly lethal and if left untreated a person may die within weeks or months after setting of the diagnosis.
Acute myeloid leukemia can be classified into several subtypes. Treatment and prognosis generally depend on the specific type. 5- year survival rate ranges from 15 to 70% and relapse affects 33-78% of all patients (once again the fact that depends on the type).
Acute myeloid leukemia is treated with chemotherapy. One more treatment modality includes hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
What are Symptoms of Acute Myeloid Leukemia?
Almost all symptoms of acute myeloid leukemia develop as a consequence of the presence of cancer cells in the bone marrow and damage to normal bone marrow cells.
The person suffering from this type of leukemia looks pale, is tired and feels breathless. The previous three symptoms are associated with lack of red blood cells (anemia). Insufficient production of red blood cells leads to inadequate supply of body cells with oxygen. Furthermore, there is an insufficient amount of white blood cells. By having insufficient number of these cells a person becomes prone to infections. Frequent infections in people may point to inadequate number of white blood cells and may point to the presence of leukemia. Lack of platelets (blood cells in charge with proper blood coagulation) is responsible for unusual bleeding, easily bruising, bleeding gums, frequent nosebleeds and heavy periods in women. In some people there is rash made of tiny little flat and red spots in the skin of the legs and in the mouth. These changes are known as petechiae.
Additional symptoms of leukemia include fever, sweats and people generally feel run down. Apart from the previously mentioned there are several more symptoms and signs of the disease and they include aching bones, raised bluish-purple areas under the skin, swollen gums etc.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...