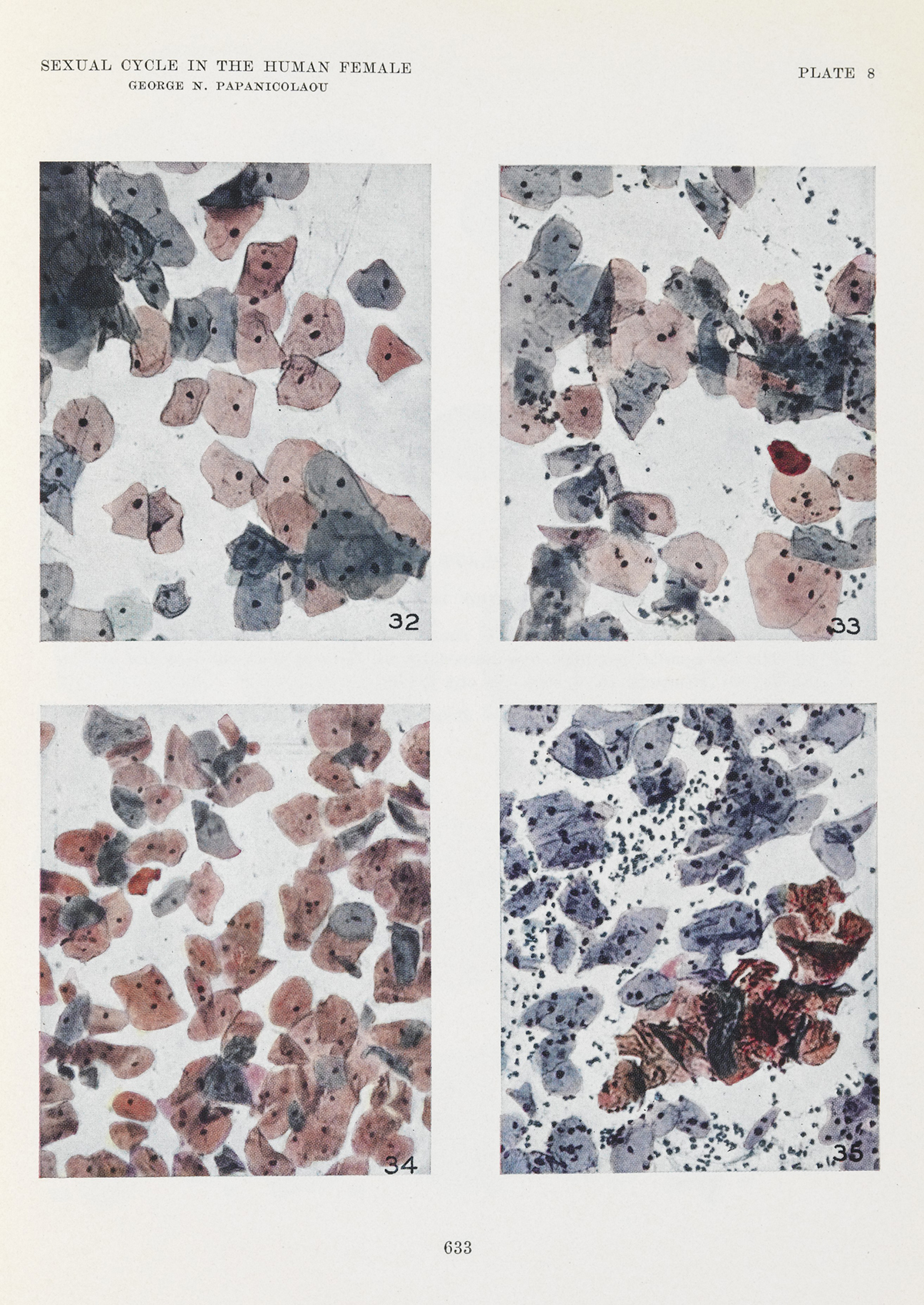
Leukopenia, or leukocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low number of the white blood cells or leukocytes. Low white blood cell count is a count below 3,500 white blood cells per microliter of blood. Pseudoleukopenia refers to temporary low white blood cell count that is common prior to outburst of an infection.
Being a part of the immune system, white blood cells provide defensive mechanism to the body against infections and diseases. There are different types of white blood cells known as granulocytes. Neutrophils and monocytes protect against bacterial and fungal infections. Eosinophils defend the body against parasitic infections. Lymphocytes produce antibodies. Basophils are involved in inflammatory reactions related to asthma and allergies. Thereby, reduction in number of granulocytes makes a person susceptible to many medical conditions.
Causes of LeukopeniaLeukopenia can be caused by many factors. It can be due to prolonged use of drugs that lower white blood cells count such as antipsychotics, antidepressants, immunosuppressant medications, diuretics and antibiotics. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy can also reduce number of white blood cells. White blood cells are produced in the bone marrow and reduction in their number can be due to diseases that damage or disrupt function of the bone marrow. That includes viral infections and congenital disorders. Autoimmune disorders such as lupus, aplastic anemia and rheumatoid arthritis can cause decrease in white blood cells. HIV/AIDS, leukemia, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, hyperthyroidism, myelofibrosis and parasitic diseases can cause leucopenia too. Sepsis and hypersplenism as well as serious allergies can lead to low white blood cell count. Finally, deficiency in nutrients such as copper and zinc can trigger leucopenia.
Symptoms of Leukopenia
Leukopenia is commonly indicated by neutropenia, subtype of leucopenia characterized by reduced number of neutrophils. Leukopenia can cause thrombocytopenia which is abnormally low number of platelets in the blood. Symptoms of leucopenia depend on underlying condition and its severity. Most commonly affected person will experience fatigue, fever, headache, hot flashes and irritability. Person with leukopenia may develop infections due to impaired immune system such as pneumonia, stomatitis and oral ulcers. Women with leucopenia may suffer from metrorrhaggia and menorrhagia.
Treatment of LeukopeniaLeukopenia can be diagnosed by complete blood count test (CBC). When CBC test shows low white blood cell count a doctor will determine what treatment will be the best depending on the cause of leucopenia. Steroids and vitamins are given to activate the bone marrow to produce more white blood cells. In some cases, chemotherapy and cytokine therapy can be used. Additionally, patient suffering from leucopenia must take necessary precautions to avoid infections.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...