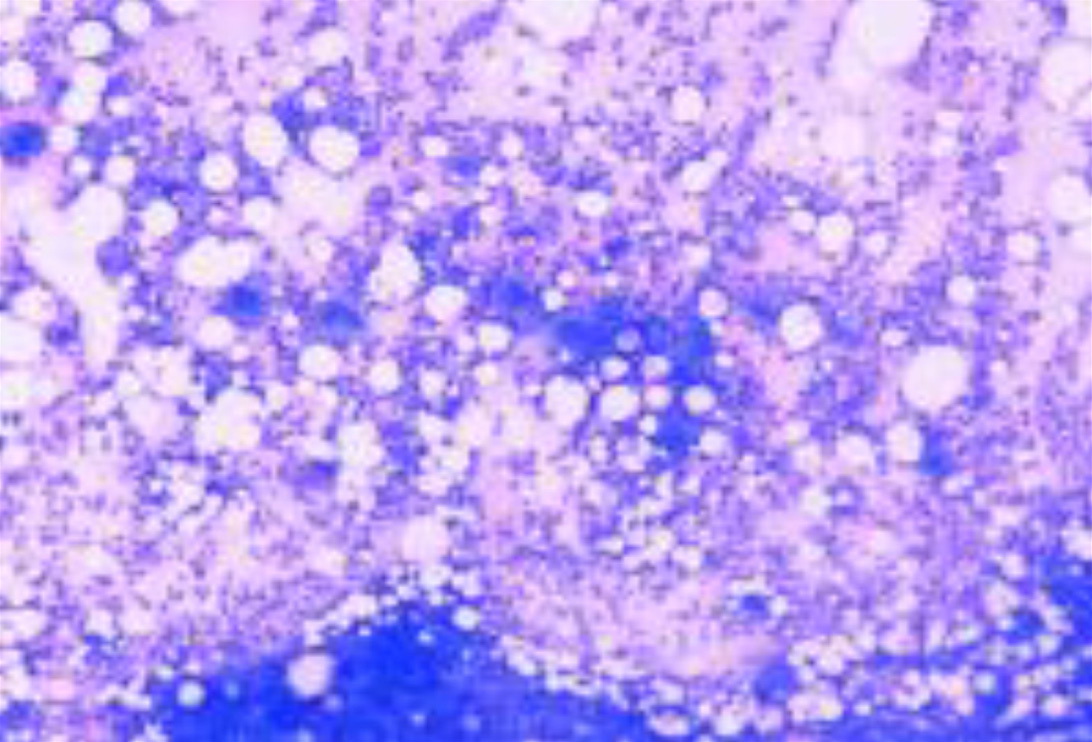
Thrombocytopenia is a medical term for low number of thrombocytes. This condition is also known as low platelet count. Thrombocytes or platelets are blood cells and they are engaged in process of blood coagulation. In order to perform their role appropriately their number needs to be optimal. Any decrease in number of thrombocytes leads to inappropriate blood coagulation and specific symptoms and signs. Namely, if one suffers from thrombocytopenia and there is even the slightest injury of small blood vessels the bleeding cannot be stopped and this may lead to serious complications.
Causes of Thrombocytopenia
All the causes of thrombocytopenia can be classified into three groups. The first one is associated with impaired production of thrombocytes. The second group includes illnesses and factors which contribute to increased destruction of thrombocytes and finally, the third group is related to splenic sequestration.
Impaired production of thrombocytes is a consequence of certain problems of the bone marrow. It may result from infections caused by a variety of viruses such as parvovirus, rubella, mumps, hepatitis C, HIV, Epstein-Barr virus etc. Apart from that reduced platelet production occurs in aplastic anemia and may be caused by certain medications and radiation. It is also a characteristic of Fanconi's anemia, a congenital disorder.
Increased platelet destruction occurs due to immunologic and non-immunologic mechanisms. Immunologic mechanism of increased platelet destruction is evident after intake of certain medications, transfusion reactions or it is associated with rheumatologic conditions. This mechanism is also typical for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Non-immunologic platelet reduction is associated with many illnesses such as sepsis, disseminated intravascular coagulation etc.
Splenic sequestration is a consequence of liver cirrhosis, leukemia and several more conditions. Once the spleen becomes enlarged it captures and sequesters more platelets than normal and leads to low platelet count.
Symptoms of Thrombocytopenia
The symptoms of thrombocytopenia are in majority of cases associated with the underlying condition. Excessive bleeding is a typical symptom which develops due to thrombocytopenia. Excessive bleeding after injuries such as cuts occurs once the number of platelets drops below 10.000 to 20.000. And in case the number is even more reduced one may experience spontaneous bleeding. Spontaneous bleeding caused by severe reduction in number of platelets features with tiny, pinpoint red flat spots called petechiae. In severe cases the skin and mucous membranes may be also covered with purpuric changes.
Treatment for Thrombocytopenia
The treatment for thrombocytopenia basically depends on the underlying cause and the number of thrombocytes. Small drop in number of platelets does not require platelet transfusion. Platelet transfusions are reserved only for patients in who the number of platelets drops below 20,000. to 50,000. Treatment of the underlying condition usually results in normalization of platelet count.
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000586.htm
- medlineplus.gov/plateletdisorders.html
- Photo courtesy of Libertas Academica by Flickr: www.flickr.com/photos/libertasacademica/8649858225/












Your thoughts on this
Loading...