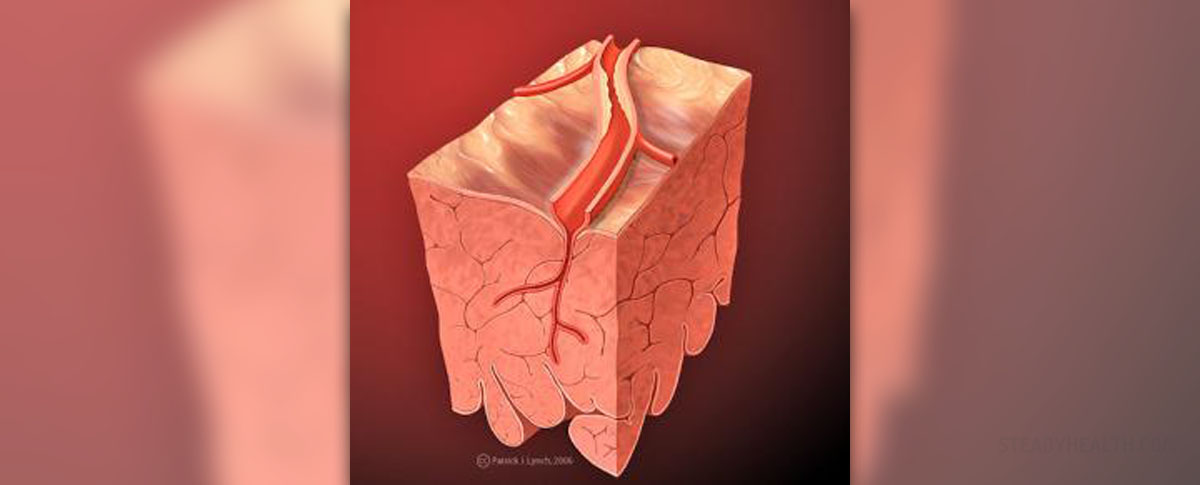
Plaque in arteries is medically known as atheroma. This is swelling of the artery walls caused by accumulation of specific substances. Plaque in arteries is made from various substances that normally circulate in the blood. Some of them are calcium, fat, cholesterol, fibrin and cellular. Once these substances start to accumulate and the plaque starts to build-up, the cells of the affected artery begin to multiply and produce several more substances which only stimulate further progression of the disease. Once the plaque deposits appear this condition is called atherosclerosis. The overall effects of the plaque in arteries are their narrowing and loss of elasticity.
Causes of Plaque in Arteries
As it has already been mentioned plaque is made of many substances. Scientists are not sure what exactly starts the process of plaque formation. There is a general belief that damage to the arterial wall represents a trigger for plaque formation.
The damage may result from high levels of so called bad cholesterol, high blood pressure and cigarette smoking. High levels of 'bad' cholesterol are considered major contributors to the formation of plaque. Furthermore, elevated blood pressure can damage the arteries and induce plaque formation. Plaque in arteries usually starts developing in childhood and teenage years and complete clogging of the arteries is evident in middle years or even later.
Symptoms of Plaque in Arteries
The symptoms of plaque in arteries basically depend on the size and location of the plaque. In early stages both plaque formation and later atherosclerosis are asymptomatic. However, once the plaque has grown to certain size the symptoms become more obvious. Large plaques cause partial or total obstruction of blood. If this obstruction develops in arteries of the arms and legs one develops peripheral artery occlusive disease. Symptoms in this case include pain, weakness, numbness or cramping in the affected extremity. Due to insufficient supply of blood to the extremities patients eventually develop sores, wounds or ulcers and noticeable change in color and temperature of the affected skin. Plaque in coronary arteries may eventually cause heart attack and accompanying symptoms while plaque in cerebral arteries is associated with transitory ischemic attack and stroke.
Treatment for Plaque in Arteries
The treatment for plaque in arteries depends on the degree of narrowing. If plaques are severe they are treated surgically. Patients may undergo several surgical procedures such as minimally invasive angioplasty, bypass surgery etc.
Patients with plaque inside coronary arteries and symptomatic angina can be treated with certain medications (nitroglycerine). Still, the best way to reverse the process and prevent plaque formation is to make lifestyle changes. These changes include well balanced and healthy diet, regular physical activity and elimination of all the bad habits (smoking, alcohol consumption etc.).











Your thoughts on this
Loading...