Angina - Overview
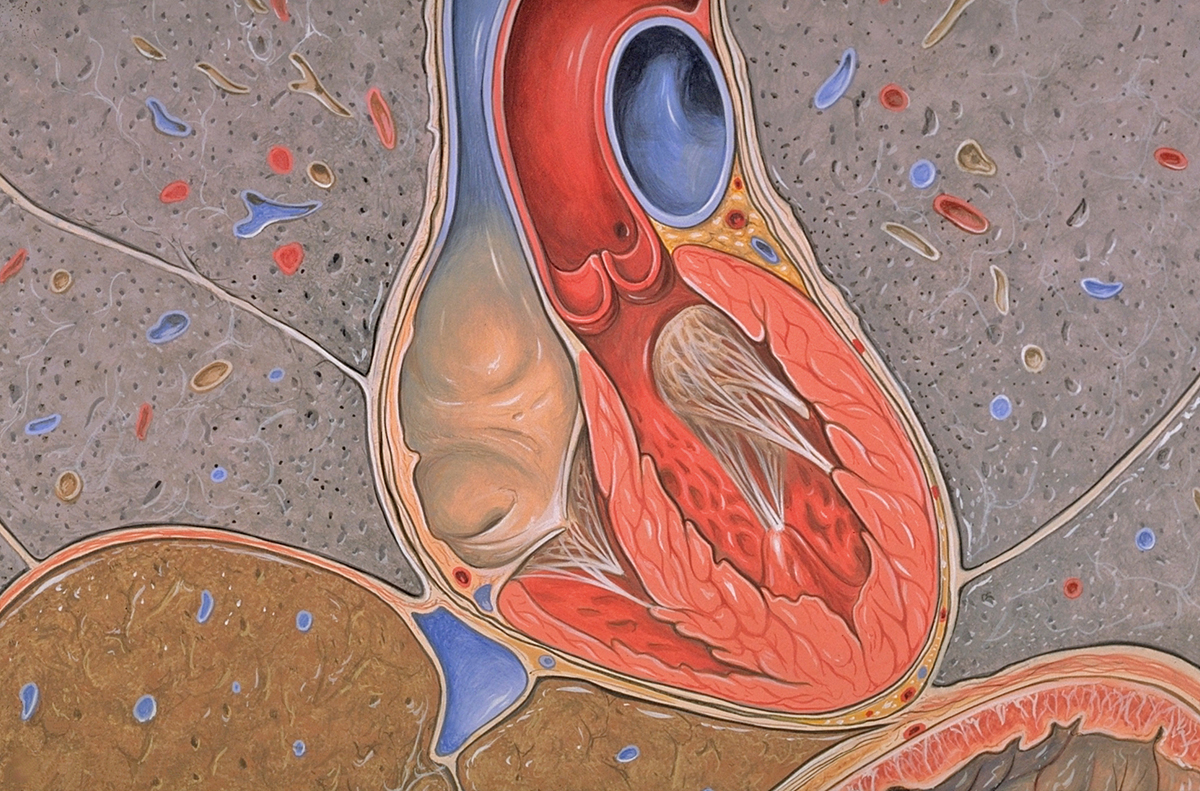
An angina is a medical condition which resembles heart attack but there is difference between the two. It can be defined as a heart condition which occurs due to ischemia of the heart muscle caused by narrowing or spasm of the coronary arteries. Angina attack typically features with a squeezing sensation in the chest and feeling of the discomfort or pain. The very attack points to the fact that the heart is not functioning properly.
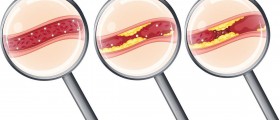
Angina mostly develops as a consequence of coronary heart disease in which the coronary arteries become narrowed due to formation of plaques (specific deposits made of fatty deposits, cholesterol, calcium, fibrin and platelets). In such conditions oxygen simply cannot be supplied in desirable amount to the heart, especially if there is increased need for oxygen (physical activity, stress etc.) and the symptoms occur. Furthermore, one type of angina called Prinzmetal's angina basically occurs due to spasm of the coronary arteries and this is another cause of this serious disease.
Symptoms of Angina Attack
Typical symptom of angina attack is pain in the chest which is usually described as tightness or heaviness in the chest. The pain is located in the middle of the chest and is most commonly induced by exercises, walking after meals, sudden change of temperature or by emotional stress. The pain may also radiate towards the neck, shoulders, jaw and down the arms. Apart from pain angina attack is accompanied by breathing difficulties and excessive sweating. The symptoms of angina attack last approximately a few minutes.
Difference between Angina and Heart Attack
In angina symptoms are connected to transitory myocardial ischemia. Angina attack develops when the heart does not receive proper amount of oxygen. While resting the heart does not require increased amount of oxygen. But in certain situations such as physical exertion and emotional excitements the heart beats faster and for this it requires additional amount of oxygen. Since the arteries simply cannot supply the heart with desirable amount of oxygen angina attack occurs. Fortunately, the very attack does not leave permanent damage to the heart muscle.
Heart attack, on the other hand, is caused by complete lack of blood supply of the particular portion of the heart. This is not caused by narrowing of the coronary arteries. Heart attack occurs due to complete blockage of the coronary arteries. The pain in heart attack is more intensive and it lasts longer comparing to angina attack and the damage to the affected heart muscle is permanent.
Treatment for Angina Attack
Angina attack requires prompt administration of a nitrate drug. This drug is available in a form of spray and tablet and alleviates the pain. Once the symptoms have been brought under control the patients are examined and then prescribed proper treatment which will prevent further attacks. In severe cases prevention of repeated attacks requires surgery.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...