Vasculitis
Vasculitis is an inflammation of blood vessels. The process of inflammation can affect each and every blood vessel starting from the smallest ones called capillaries to the largest blood vessels, arteries and veins. In case that vasculitis reduces the blood supply to certain tissue, the tissue will suffer consequences of hypoxygenation and eventually die.
In some cases vasculitis is limited process and affects only certain organs. This type of vasculitis can affect the skin, the eyes or brain and some other organs. On the other hand, there are types of vasculitis which tend to affect several organs and organ systems. This form of vasculitis is classified as general vasculitis and it ranges from mild forms to severe cases of disease.
The symptoms vary according to the type of vasculitis and the affected organ. Systemic symptoms include increased body temperature, loss of appetite and consequent weight loss, tiredness and general pain and aches.
Causes of Vasculitis
In majority of cases the actual cause of blood vessel inflammation cannot be found. Vasculitis is in this case classified as idiopathic.
Still, in other cases vasculitis is strongly related to abnormal response of immune system. Many forms of vascilitis are actually autoimmune diseases. The diseases can be triggered by certain allergens and infections, especially viral infections. Vasculitis can also be one of the characteristics of numerous autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's syndrome or rheumatoid arthritis.
Complications of Vasculitis
In certain cases the wall of the inflamed blood vessels can weaken to such extent that aneurysm occurs. Aneurisms may eventually burst and lead to serious hemorrhage.
The process of inflammation regularly narrows the affected blood vessels and the organ that is supplied by this affected blood vessel may suffer from insufficient amount of nutrients and oxygen.
Diagnosing Vasculitis
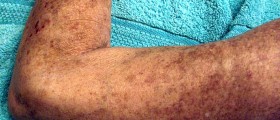
In case that process of inflammation affects the skin even the patient can notice skin changes. They include clusters of small dots, red spots or red bumps, bruises, and hives. Itching can be accompanying symptoms of the disease.
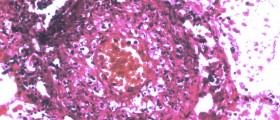
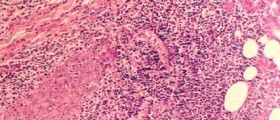
In some cases setting of the diagnosis can be rather difficult. The definitive diagnosis can be set after the affected organ has been biopted and the sample has been pathohistologically examined.
If the process of inflammation affects particular organs the blood vessels of these organs are pathohistologically examined. The doctor needs to find the underlying cause of the disease and to treat it. This way the symptoms of vasculitis can be brought under control. This particularly refers to autoimmune diseases in which vasculitis occurs commonly.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...