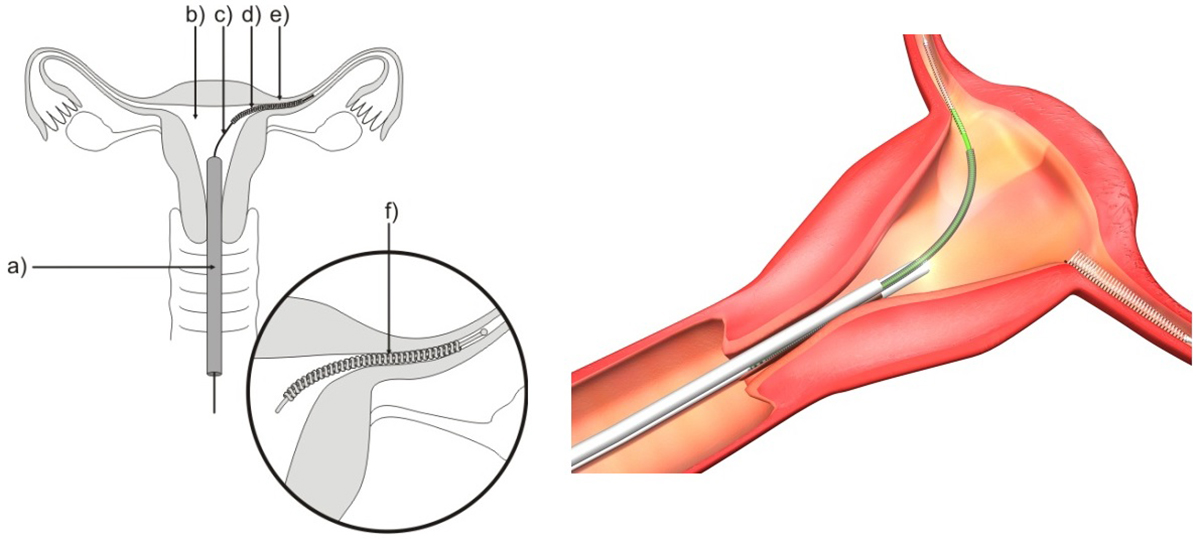
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a procedure used to examine uterine cavity. Hysteroscopy is performed using a tube with thin telescope, called hysteroscope, inserted through the cervix into the uterus. Received images are sent to computer that captures and records details of the womb. It is useful in diagnostics of uterine conditions. Hysteroscopy is an out-patient procedure that doesn’t require staying in hospital longer than one day. If a hysteroscopy is done without anesthetics you may take some painkillers prior to procedure.
If you are pregnant or suffer from vaginal or urinary tract infections or uterine cancer, you shouldn’t undergo hysteroscopy.
Alternatives to hysteroscopy can be more suitable depending on the symptoms and circumstances. Alternatives include pelvic ultrasound and endometrial aspiration.
Complications of hysteroscopy are very rare, severe complications occur in less then 1% of cases. Possible complication of hysteroscopy can be uterine perforation which leads to bleeding. Other complications involve cervical laceration, intrauterine infection, electrical and laser injuries.
Types of Hysteroscopy
There are two types of hysteroscopy: diagnostic and operative hysteroscopy.
Diagnostic Hysteroscopy
Diagnostic hysteroscopy aims to diagnose problems of the uterus such as uterine polyps, fibroids, uterine septum, etc. This procedure can be done with or without local anesthetics. Diagnostic hysteroscopy is used to search for the womb abnormalities and causes of certain symptoms. These symptoms involve irregular or heavy periods, pelvic pain, unusual vaginal bleeding or discharge, recurring miscarriage or infertility.
Operative Hysteroscopy
Operative hysteroscopy is usually performed in the operative room under general anesthesia. Hysteroscopy is operative when additional procedures must be done, such as biopsy or treatment. Biopsy is small sample of tissue taken for examination in laboratory. Biopsy is taken when a surgeon notices any abnormality in the womb. Treatments that are commonly conducted during hysteroscopy include removal of fibroids, polyps, stuck or lost intra-uterine contraceptive device or adhesions and scar tissue in the womb. These can be removed by using electrical and mechanical hysteroscopic instruments.
Hysteroscopy ProcedureThis procedure usually lasts from 10 to 30 minutes depending on what has to be done. Surgeon firstly takes speculum to gently open the cervix. The speculum is a device that is inserted into vagina to help the view the cervix, entrance of the womb. After that, surgeon cleans the vagina and cervix with an antiseptic solution and passes the hysteroscope through the cervix into the uterus. To expand the womb, surgeon may pump gas or fluid inside. The camera attached to hysteroscope sends pictures from the inside of the womb to a computer. If biopsy must be taken or any treatment is required, surgeon will pass other instruments into the womb.





_f_280x120.jpg)






Your thoughts on this
Loading...