Introduction
Female reproductive organs are susceptible to the variety of infections which can lead to developing severe medical conditions. The availability of different treatments may cure, but sometimes the surgery can be the only help. Doctor will always prescribe nonsurgical treatments before considering the possibility of the surgery. One of the hardest surgeries to endure for women is probably hysterectomy, the removal of the uterus or womb. After hysterectomy a woman cannot get pregnant. Menstrual periods discontinue and the recovery lasts for a long time. Hormonal imbalances occur so the woman enters the surgical menopause. If the ovaries have not been taken out by hysterectomy then the woman gets into the menopause a few years after. Hysterectomy is done in a few circumstances, to the women with fibroids, the benign tumors, cervical, uterine, and ovarian cancers of the Fallopian tubes, but also in the cases of serious pelvic complications. The Procedure
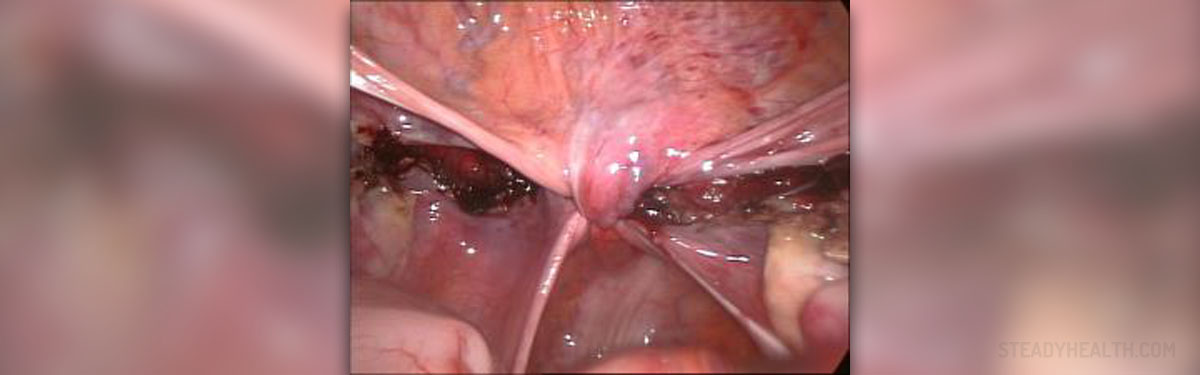
The surgery is one of the most often performed ones. One in three women has had the operation some time in life. The surgery Doctors conduct different hysterectomy types depending on the individual characteristics of the condition. Hysterectomy may be total by which the surgeon removes the whole uterus and the cervix. Subtotal hysterectomy means the removal of the uterus but the cervix remains. The surgery may be carried out so as to remove the great part of the female organs, so together with the removal of the uterus and the cervix, a surgeon removes the Fallopian tubes and ovaries. This kind of operation is called total hysterectomy with the salpingectomy and oophorectomy. Radical hysterectomy takes out the uterus and its tissues, parts of the vagina, ovaries, tubes and lymph glands. The surgery may be performed by making an incision on the vagina, lower abdominal area or by making several incisions on the stomach.
Risks
As well with other types of surgeries, the hysterectomy bears the risk the general anesthesia has. General anesthesia may impair the nerve cells and be fatal. Extensive bleeding is possible complication in which case the blood transfusion is necessary. There is the risk of infection after the surgery, mostly urinary and vaginal infections. A woman's bowel or bladder may be affected so she may have problems with bowel emptying and urinating. As a consequence of this, the catheter is placed or colostomy done. Some time after the surgery, adverse affect may develop, like vaginal prolapse where the part of the vaginal canal sticks out of the vagina. If the ovaries remained after the hysterectomy, they will however stop functioning some time after the operation. There is no more ovulation and the menopause begins. The woman suffers from insomnia, has sudden mood changes, hot flashes and profuse sweating and is likely to develop osteoporosis. Occasionally, blood clots can appear and disable the blood circulation.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...