Most terminations of pregnancy take place within the first trimester — the time that would begin the day the person misses their menstrual period and lasts through week 12 after conception. The second trimester begins on week 12. A pregnant person may have an abortion at this time because they were still deciding on their options, or were arranging access to an abortion. What can generally be expected from a termination of pregnancy at this time?
Abortion procedure at 12 weeks
A medical abortion, in which the pregnant person takes two different medications to end the pregnancy, is available until the tenth week. This means that, 12 weeks into a pregnancy, a medical abortion is not an option anymore, and a surgical abortion will be required. These procedures are also called an aspiration abortion, suction abortion, suction curettage, or vacuum aspiration.
Suction aspiration uses aspiration to remove the contents found in the uterine cavity through the cervix. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus that protrudes through the upper anterior vaginal wall. The procedure is quick and usually involves a clinical visit of up to several hours, including time spent in the waiting room. The very procedure lasts no more than 15 minutes, but before the termination, pregnant people will be asked to fill out forms and confirm that they have freely decided on having an abortion. A basic health examination, including weighing, can also be expected.
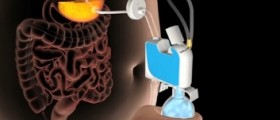
During an abortion procedure on the cusp of the second trimester, the surgeon uses suction tools: an electric or manual pump, depending on the preferred method and availability. Both are equally safe and efficient, and are routine procedures. In most cases, the doctor will use a local anesthetic agent to numb the region and dilators to pen the cervix. A sterile cannula, which is a tube used for removal of the fluid and other contents, is then inserted into the body and attached to the pump. The pump creates vacuum that sucks out the uterine contents, leaving it empty.
After the procedure, the patient will be given time to recover from the anesthesia, given some juice and a cookie (just like after blood donation), and provided with sanitary pads. Patients can expect some cramping and discomfort in the following days, along with bleeding that can be compared to a menstrual period. Although the rate of infection is low, it is important to look out for signs of infection — such as fever, increasing abdominal discomfort, and pus-filled (green or yellow) discharge. Your provider will offer you instructions on post-procedure aftercare, and may ask you to return for a follow-up visit in a few weeks.
Safety
This procedure is very safe. After every suction aspiration, doctors examining the evacuated contents of the uterus and perform an examination to check that the uterus is now empty. Suction aspiration has the lowest rate of infection, when compared to any other surgical abortion procedure. The rate of infection for this procedure is 0.5% when carried out in reputable facilities. The procedure is 98% effective in removing all uterine contents. The complications are rare and include excessive blood loss, infection, injury to the cervix or uterus, perforation and uterine adhesions.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...