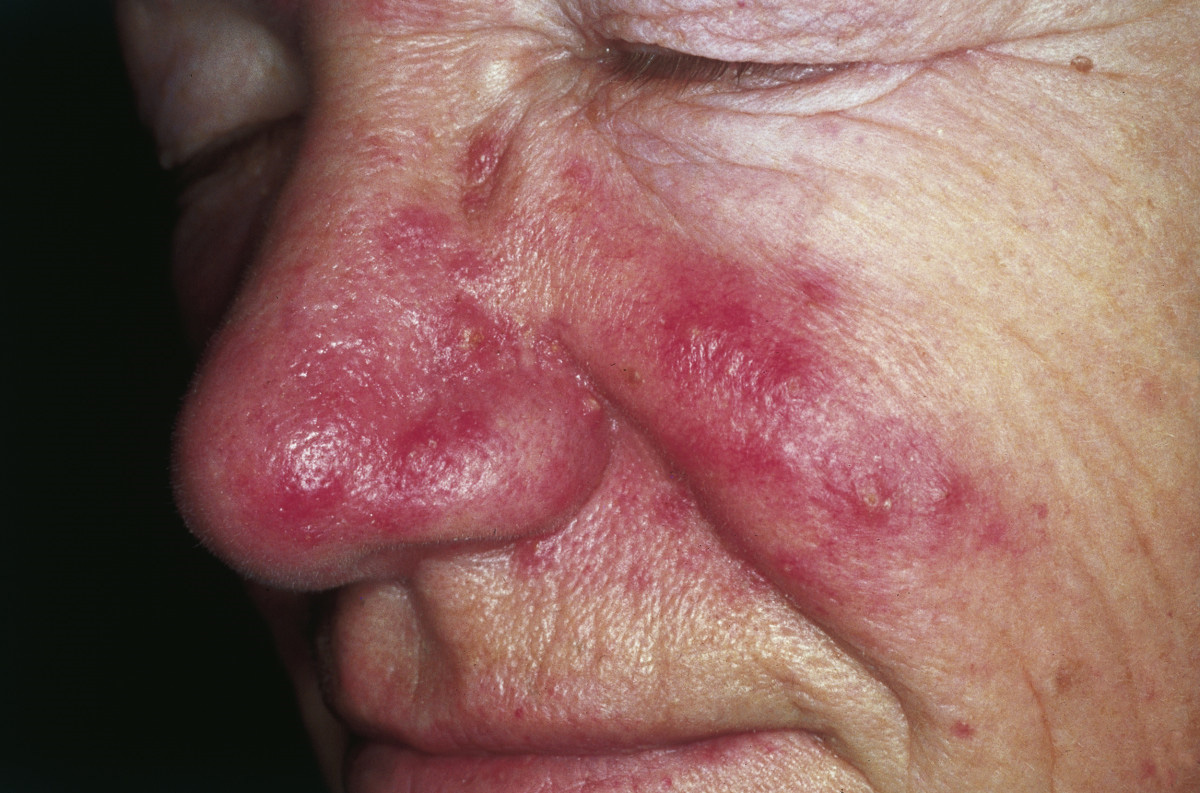
Rosacea is a chronic health condition that affects the facial skin and manifests in redness, often accompanied with pimples. The condition is usually harmless but aesthetically unappealing. Commonly, the condition is mistaken for severe acne problem, since it commonly involves the formation of small red bumps and pustules. The redness typically begins on the central portion of the face across the cheeks, nose or forehead, and less commonly affects the neck, chest, ears and scalp. Ocular rosacea is a more severe manifestation of this disease. It typically affects the eyes and the eyelids causing a lot of discomfort to the patient.
Symptoms of ocular rosacea
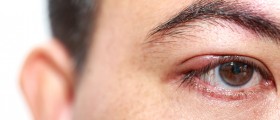
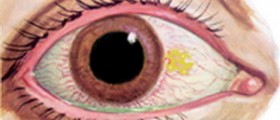
Ocular rosacea is diagnosed when the patient has one or more of the common symptoms: watery or bloodshot appearance of the eyes, foreign body sensation, burning or stinging sensation, dryness of the eyes, itching, increased sensitivity to light, blurred vision, telangiectases of the conjunctiva and lid margin, or lid and periocular erythema. Ocular rosacea commonly develops along with the skin rosacea. However, in some patients it may develop completely on its own. In about 20% of all cases, ocular rosacea begins before any kind of skin problems. The eyelids may also become swollen, and styes are common.
Causes of ocular rosacea
Like skin rosacea, the exact cause of ocular rosacea is yet unknown. Scientists believe that many hereditary and environmental factors working together cause the development of this disease in some people. Among the most possible causes, doctors commonly include consuming very hot or spicy foods and beverages, drinking too much alcohol or caffeine-rich drinks. Being in the extreme cold or heat, or being exposed to a lot of sunlight may also provoke the ocular rosacea. Similarly, taking hot baths or being in saunas is considered one of the major risk factors. People who are very stressed, angry or often embarrassed can also develop this health problem. Other causes include taking corticosteroids, exercising strenuously and taking certain medications that can dilate the blood vessels.
Complications of ocular rosacea
Unlike the skin rosacea, ocular rosacea is a potentially dangerous condition that demands medical treatment. Untreated ocular rosacea may affect the surface of the eye and gradually cause problems in vision that can lead to vision loss. The complications are more common in patients who have dry eyes, and often result in inflammation of the eyelids and secondary infection of the cornea.
Treatment of ocular rosacea
There is no cure for ocular rosacea but there is a treatment aimed to manage the condition. In most severe cases, doctors will prescribe oral antibiotics or temporary use of oral corticosteroids to reduce the inflammation. Artificial tears may help to remove the dryness and lessen the redness of the eyes.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...