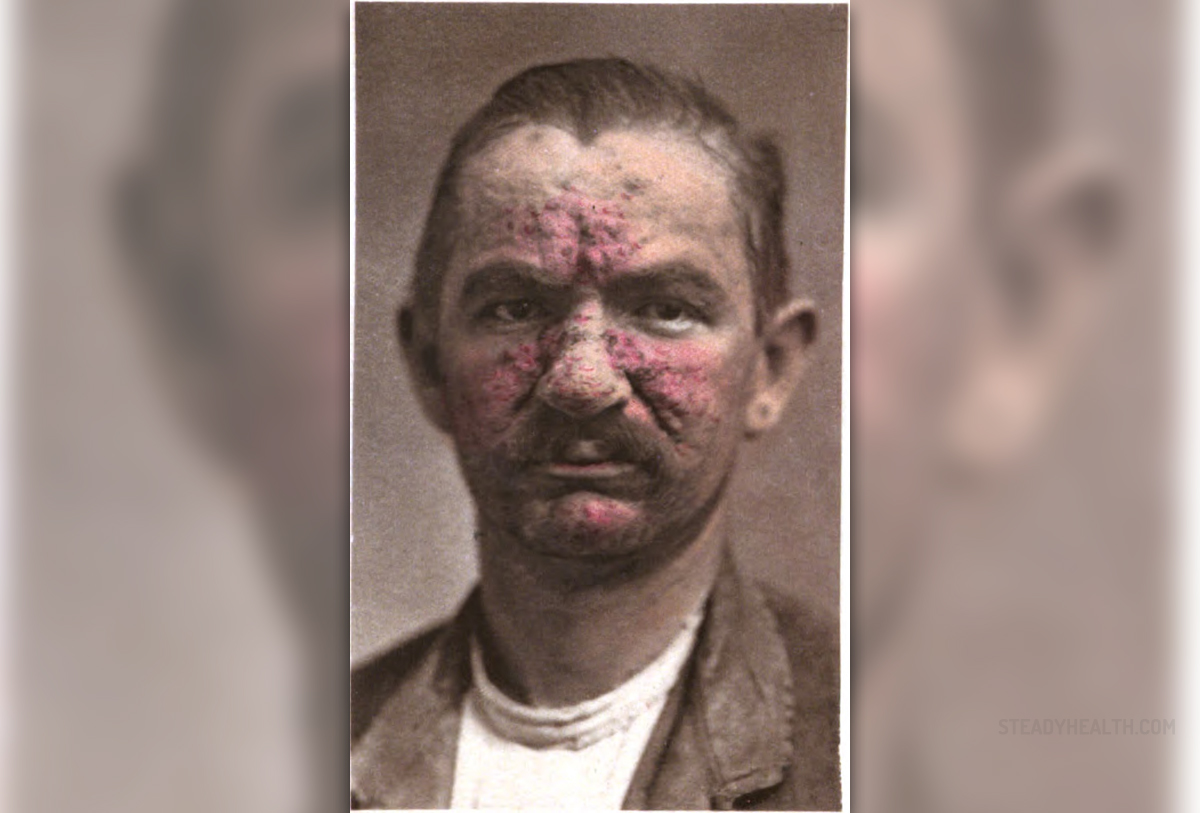

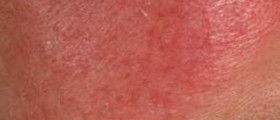
Rosacea is a chronic skin disease that sometimes affects the eyes as well. It usually affects the face but it can be diagnosed on other parts of the upper body as well. This condition is characterized by a redness of the skin, pimples or similar bumps and sometimes thickness of the skin.
Rosacea is quite common. It is estimated that 14 million Americans have this disease. It is more frequent in women, especially in menopause. Despite its frequency, it often goes undiagnosed. It affects all skin colors, although it is more frequent in people with light skin.
The symptoms of rosacea include frequent or constant redness of the skin, with a burning sensation and swelling. Small red lines may appear under the skin and that area may become red, warm and swollen. Those lines are in fact enlarged blood vessels. Thickening skin is another symptom of rosacea.
Skin may have small bumps, sometimes filled with puss. They are called pustules.
Inflamed eyes and eyelids and a swollen, bumpy and red nose (especially among men) can be signs of rosacea as well.
Generally speaking, there is no definitive cure for rosacea. However, the symptoms can be treated in order to alleviate them and to give the skin a more pleasant appearance. Sometimes even good skin care and the prevention of factors that cause flare-ups is sufficient enough.
As for treatment, if the case of rosacea is a mild one, doctors usually prescribe topical antibiotics, such as benzoyl peroxide or metronidazole. Those medications are applied directly to the skin twice a day.
Azelaic acid is another possible treatment for a mild case of rosacea, but it seems to have more side effects than metronidazole.
For a severe case of rosacea, a treatment with oral antibiotics is the usual course of action. Those can be tetracycline, doxycycline or erythromycin. The oral antibiotics are very effective against pink bumps and pustules, but redness is more difficult to cure and will most likely come back. Tretinoin is another possible treatment but it is usually used in addition to oral antibiotics.
Most rosacea patients respond to antibiotics after a few months of treatment.
Ocular rosacea, the rosacea that affects the eyes, is usually treated with oral antibiotics, and in severe cases, with steroid eye drops.
Rosacea is a chronic condition in which medication should be administered regularly, not just during flare-ups. It may take up to several months to see visible improvement, but if it is left untreated, rosacea may cause a rather disfiguring appearance.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...