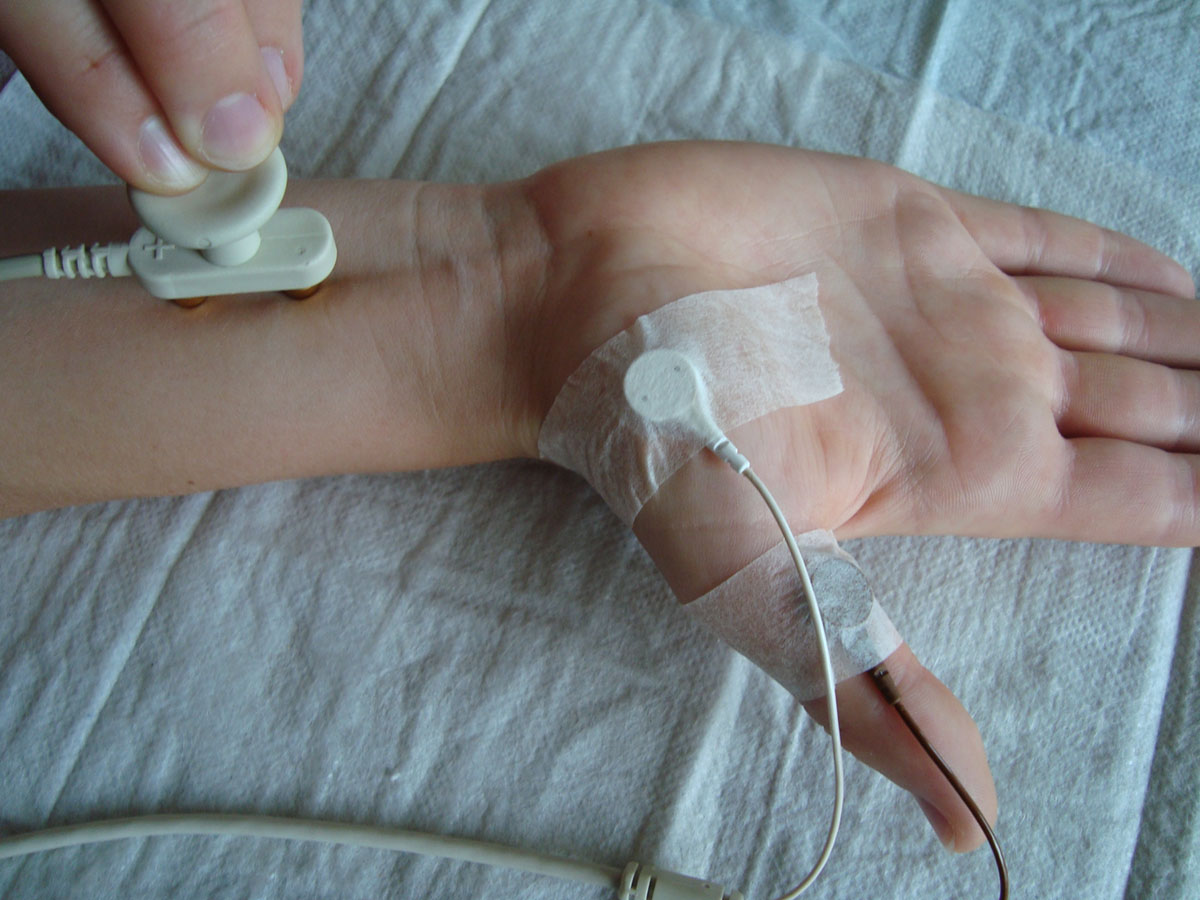
Nerve conduction velocity test is a form of electrical test which serves the purpose of determining whether one's nerve impulses are conducted properly or not. Therefore, if there are damages affecting the nerves, this test is going to detect them.
The nerve conduction velocity test is performed by stimulating the nerve so that it releases an electric impulse which is later measured. In order for this to be possible, electrodes are placed on the surface of the skin of the patient. The place of application of these electrode patches can vary.
Nerve Conduction Velocity Test
The electrodes used for this testing are similar to those used during a regular ECG testing and each patch provides different information about the electrical activity of the impulse stimulating the nerve. In order for the test to be more effective and thorough, it is commonly combined with electromyography, taking information from needles which are placed inside the muscle tissue.
The nerve conduction velocity test is not painful, even though you might experience mild shocking sensations, depending on the strength of the stimulus. However, by the end of the testing, you should not feel any forms of discomfort or pain. Yet, the electromyography may result in muscle spasms. Also, once this test is done, the muscles which were exposed to the needles may be sore for a while.
It is crucial that you maintain normal body temperature during the nerve conduction velocity test and your doctor will do his/her best to assist you with this. Low body temperature slows down the nerve conduction and, thereby, leads to inadequate results.
Moreover, you need to inform your doctor if you have a pacemaker in your body or a cardiac defibrillator device, since certain modifications will need to be done to the testing in order for it to be safe for your health.
Normal test results can vary, depending on the age of the patients and even the laboratory where this test is carried out. Nevertheless, your doctor will known how to interpret the results of your nerve conduction velocity test so that you can understand them completely. In order for the results of babies to be considered normal, these need to be at least 50% smaller than normal results for adults. However, the adult values are expected after the child is 3 or 4 years old.
Usually, people who experience symptoms like numbness, tingling and burning in certain parts of their body are those who have this form of testing recommended by their physicians, taking into consideration that this test can reveal conditions such as peripheral neuropathy and mononeuritis multiplex, or even carpal tunnel syndrome and compression neuropathy.
Why is the Test Done?
The main purpose of this form of testing, as it was mentioned above, is diagnosing of the level of nerve damage or destruction. Also, during the testing, various diseases of the nerves and the muscles can be detected. Some of these are myopathy, Lambert-Eaton syndrome or myasthenia gravis.
Furthermore, the nerve conduction velocity test is a recommended step to take once the patient is diagnosed with nerve lesions due to a spinal cord injury or any other form of trauma to the nerves. Additionally, people suffering from neuromuscular junction disorders need to undergo repetitive nerve stimulation as a part of this testing.
Also, the nerve conduction test is very useful during the diagnosis of muscle disorders such as myositis or myopathy, as well as some generalized neuropathies, encompassing uremic, metabolic and immune variants of this disease.
Some other suitable patients for this form of testing are people who show symptoms such as pain in joints or limbs, general weakness or fatigue, cramps or twitching.
However, nerve conduction velocity test can be an effective tool for the diagnosis of many other conditions. Yet, if this test is not suitable, then the electromyography is conducted. Still, doctor's should not perform this invasive test on people who are on anticoagulant therapies with warfarin and direct thrombin inhibitors.
Most of these conditions require regular testing of this type, administered once or twice during every year of the treatment. This way, doctors can monitor the progress of the patient and rest assured that the therapy is taking the adequatecourse.
Finally, the nerve conduction velocity test can also be done for the purpose of diagnosing conditions which are related to the carpal tunnel syndrome such as tarsal tunnel syndrome, nerve root compression, neuritis, motor neuropathy, mononeuropathy, radiculopathy and plexopathy.
All in all, the nerve conduction velocity test is a very useful diagnostic tool used for determining the levels of nerve damage in one's organism. The test is carried out by placing electrodes on certain parts of the patient's body. The electrodes are connected to a computer which collects the data and displays the results. Therefore, if there are any problems with the conduction velocity of the nerves, this test will reveal it.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...