
Tarsal tunnel syndrome
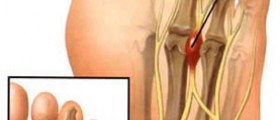
Symptoms of this syndrome are felt when the ligamentthat runs inside the ankle compresses the tibial nerve, and includenumbness and burning on the heel and sole of the foot. Some peoplemay also experience tenderness behind the inner side of the ankle.History of previous injuries to the nerves or joints in this region,such ankle fractures, sprain, and cysts is common in patients thatsuffer from tarsal tunnel syndrome. It is also common in diabetessufferers.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis is based on review of the medical history andphysical examination. Confirmation of the diagnosis depends on testssuch as EMG. Tarsal tunnel syndrome should not be confused withconditions that have similar symptoms, such as a pinched nerve in thelower back, neuropathy or a tumor in the sciatic nerve. MRI scan orelectrical tests help to differentiate these conditions and determinethe exact source.
First thing that is tried is to avoid activity thatworsens the pain. Also, some relief can be obtained through use ofcomfortable walking shoes and orthotics. Patients that suffer fromnerve damage caused by diabetes (diabetic neuropathy) may try to usemedications to relieve the problem. for example, some people may feelrelief from use of steroid injections in the vicinity of the tibialnerve. If the diagnosis is definite, an attempt can be made toresolve this condition by means of decompressive surgery. Implantableperipheral nerve stimulator is used in patients with severe symptomswho experienced no improvement over previous decompressive surgery.
Surgery for tarsal tunnel syndrome
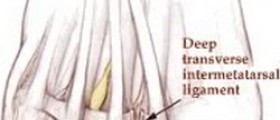
Surgery is usually performed in day surgery undergeneral anesthesia and does not require intubation. It is an analogueof the carpal tunnel surgery, the main difference that this procedureis performed on the foot. It lasts for slightly over half an hour,and is done through a two inch long incision behind the inner side ofthe ankle. The incision in the skin allows for the opening of the tarsaltunnel. The tibial nerve is then identified and followed into thefoot. All places where the nerve is compressed will be treated (forexample, cysts will be removed) so that the pressure on the nerve isremoved. Sutures stay for ten days after the surgery. Recovery takestwo or three weeks, but it might take two or three months before youfeel any improvement.
Complications related to surgery
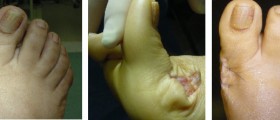
The surgery itself is a very safe procedure but it notall patients experience improvement from the surgery. Complicationsinclude infections, but such cases are rare. Some pain, tendernessand swelling are normal and will resolve within days. Intense woundpain and tenderness are problematic in patients who suffered fromsevere foot pain before the surgery.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...