The human brain is a mighty organ in charge with practically all functions in the body. It represents quite a mystery to scientist who give there best to explore all the functions and malfunctions of the organ and this way help patients suffering from various disorders affecting the central nervous system. It seems that many years will pass until we get fully informed about all our brain can do.
Measuring Electrical Activity in the Brain
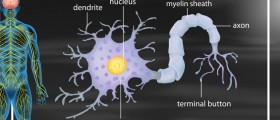
Unlike other organs in the body, the brain functions with the assistance of electrical signals and specifically designed substances called neurotransmitters, which are basically endogenous chemicals that transmit these electrical signals from a neuron to neuron.
All the information from the entire body eventually reaches the brain through the spinal cord. At the same time, the brains sends signals to the spinal cord which then stimulates various organs or inhibits their function and by doing so control them. Only visual and hearing stimuli go around the spinal cord are are transmitted directly to the brain.
The brain comprises two hemispheres. Neurons from one hemisphere are in contact with each other but there is also connection between the two hemispheres which are actually in charge of different functions but may sometimes cooperate.
Now, electrical activity in the brain is a significant parameter taken into consideration when doctors are diagnosing certain medical conditions. Such activity of the brain is easily measured with the assistance of evoked potentials. The activity triggered by stimulation of specific sensory nerve pathways is tested and the results are combined with other diagnostic tests and exams which significantly helps doctors to confirm some neurological disorders with greater certainty.
This type of testing provides with information regarding the speed and the quality of the nerve signals that reach the brain. The test is sensitive enough to indicate rather delicate problems along nerve pathways which might be overlooked or not even noticed during neurological exam. Evoked potentials are also effective in case MRI shows no structural changes but there are neurological deficits and patients experience certain symptoms.
When it comes to types of evoked potentials these are classified into visual evoked potentials, auditory evoked potentials, median nerve sensory evoked potentials, posterior tibial nerve evoked potentials and evoked potential back averaging.
Visual evoked potentials test the eyes i.e. the optic nerve along with the optic tract in the brain. During the test patient's eyes are stimulated by looking at a test pattern while electrical activity is measured with the assistance of electrodes attached to the patient's scalp and shoulder. Auditory evoked potentials measure electrical activity that occurs when hearing is stimulated. Median nerve sensory evoked potentials and posterior tibial nerve sensory evoked potentials measure electrical activity obtained by stimulation of the median nerve located near the wrist and the posterior tibial nerve located near the ankle. And finally, evoked potential back averaging is a specific test that includes electroencephalography. It records multiple jerking movements. Electrodes are in this case placed onto the scalp and the parts of the body affected by jerking movements.
Evoked Potentials in Multiple Sclerosis
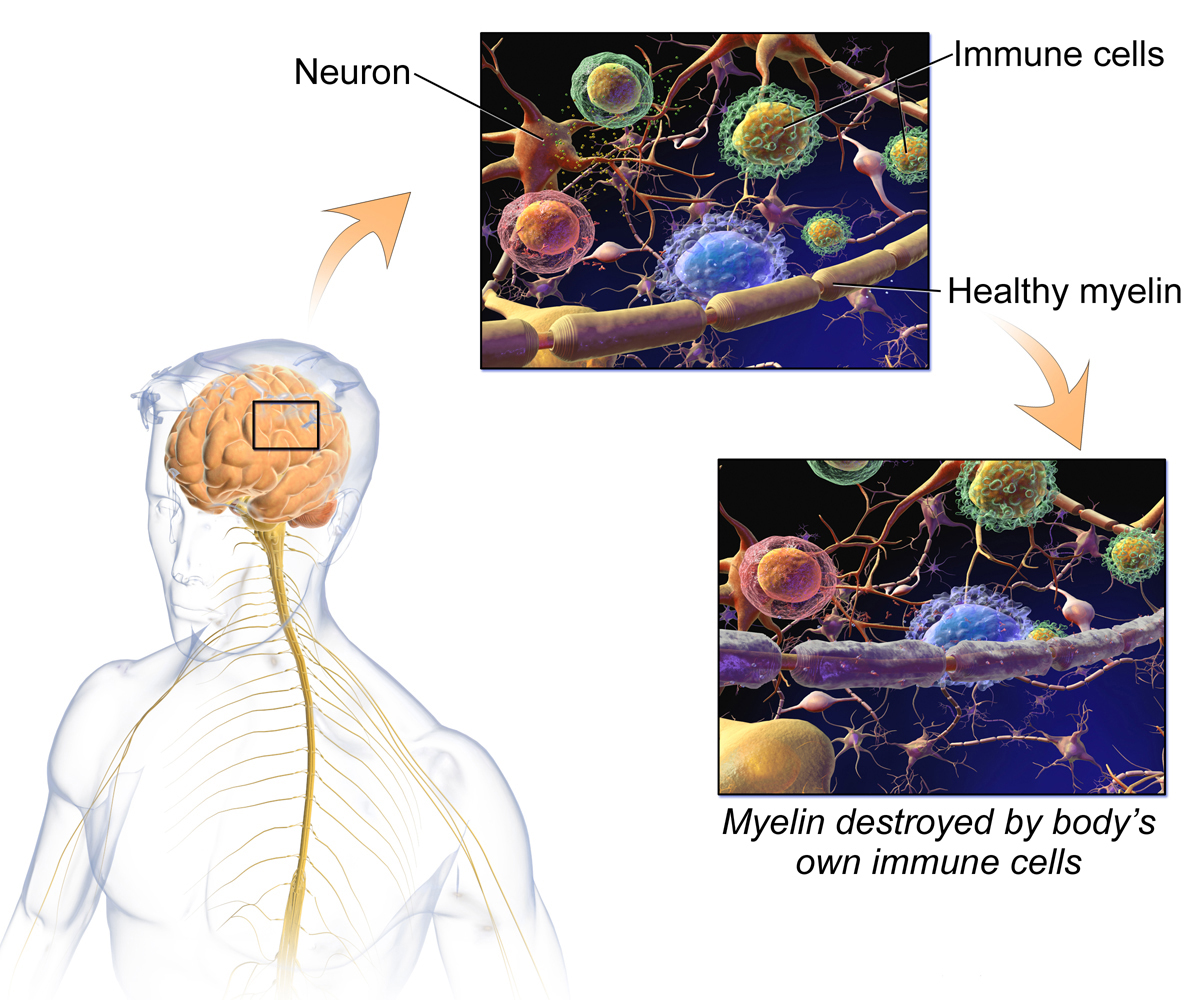
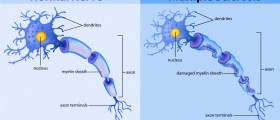
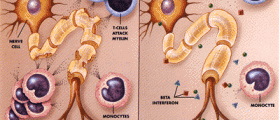
Evoked potentials are very useful diagnostic tool for multiple sclerosis (MS), a neurological disorder characterized by progressive loss of myelin sheath. Myelin sheath plays an integral part in transmission of electrical impulses across the central nervous system. In patients with MS transfer of electrical impulses is interrupted at spots where myelin is damaged. This results in various neurological deficits which tend to be even more complex in time.
The results obtained with the test are interpreted by a well experienced neurologist or neuropsychologist. The test is along with patients' medical history, laboratory findings and neurological exam as well as MRI of the brain and spinal cord taken into consideration once doctors decide on the treatment.
In practically all patients suffering from MS evoked transmission of electrical impulses is rather slow. In nerves that are partially damaged transmission is markedly delayed, but still exists. On the other hand, complete loss of myelin leads to irreversible damage to conduction of electrical impulses.
One of the greatest advantage of evoked potential in case of individuals with MS is detection of abnormalities regarding electrical activity when there are no noticeable lesions. Such results are not good because they actually inform doctors that there will eventually be symptoms related to the detected irregularities and that the lesions will eventually become clear and noticeable by imaging techniques. So, apart from being of major help when diagnosing MS, evoked potential are also highly efficient indicators of the course of the disease.
All in all, multiple sclerosis is a severe illness that leads to permanent damage to the central nervous system and interferes with many of its functions. It can be diagnosed with many available test and exams. One of these is evoked potential test. It easily confirms the presence of abnormal transmission of nerve impulses but may also predict the course of the disease and estimate its progression. By doing so, the test allows doctors to be more aggressive in treatment and try to delay some of inevitable complications of the disease.


_f_280x120.jpg)


_f_280x120.jpg)



_f_280x120.jpg)



Your thoughts on this
Loading...