
Hearing Loss
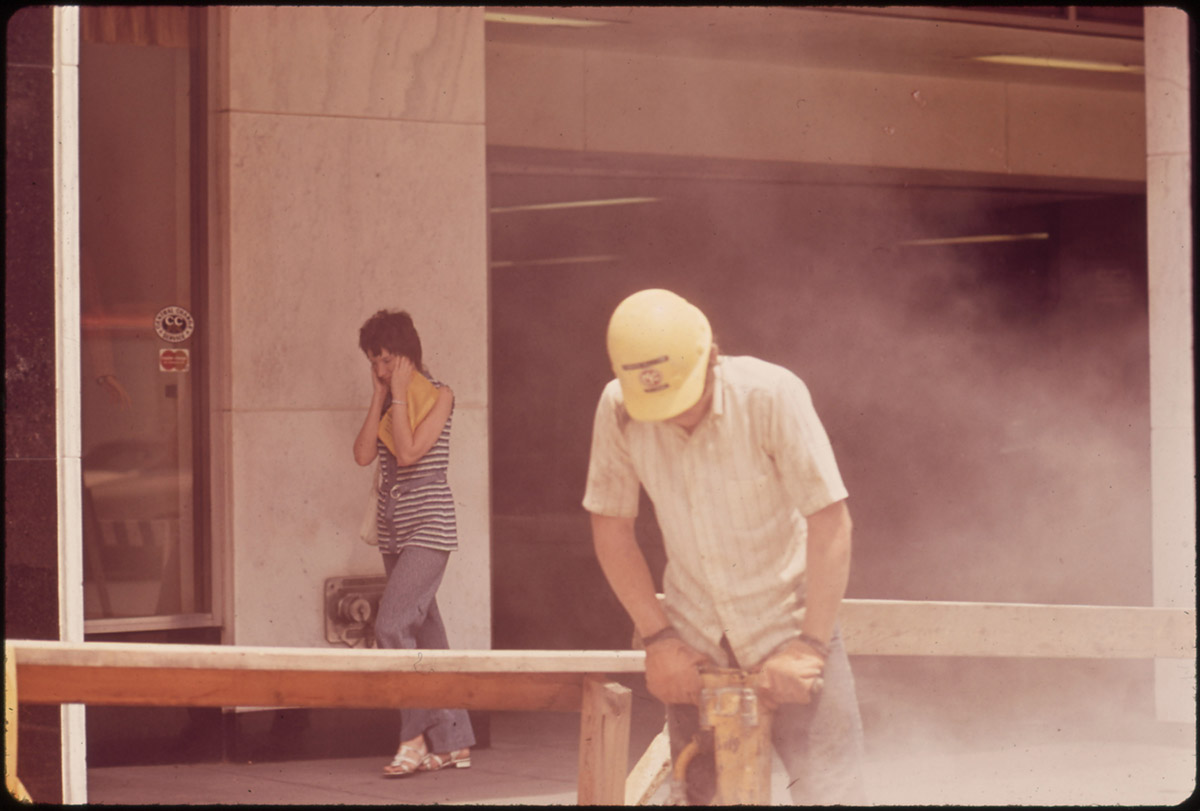
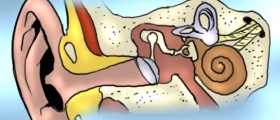
Hearing loss is caused by abnormalities in the auditory system that results in loss of sound sensitivity. Hearing loss can be a result of various different conditions. The cause of hearing loss cannot always be identified, and hearing loss can be spontaneous in some cases.Hearing loss can be conductive or sensorineural. When sound waves passage is blocked and the air cannot get to the inner ear, the hearing loss is conductive. If the auditory nerve or hair cell in the inner ear is damaged, the hearing loss is sensorineural. Sensory refers to hearing loss that occurred by abnormalities in the cochlea caused by noise damage trauma, viral infection, Meniere’s disease and drug toxicity. Neural refers to problems with the auditory nerve.Hearing loss can be partial or total and appear suddenly or gradually.
Diagnosing Hearing Loss
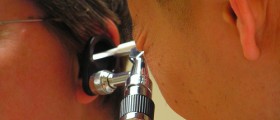
To determine the presence, location, degree, magnitude and qualities of hearing loss various examination techniques are performed. Otoscope is used to perform a physical exam. It evaluates the tympanic membrane, ear canal, nasopharynx, nose and upper respiratory tract.Air conduction tests stimulate the ear with air. These tests examine the hearing ability of external auditory canal, central auditory pathways, eighth cranial nerve, the middle ear and the integrity of inner ear.Bone conduction tests use transfer of vibration through bones. This way the external auditory canal and middle ear are bypassed and the problems in the inner ear, central auditory pathways and eight cranial nerve can be diagnosed. The tests are performed by getting a vibrating tuning fork in contact with the head.Conductive and sensorineural hearing losses can be distinguished by the Weber and Rinne tests. They both use tuning fork as the diagnose tool.Weber test is performed by using 256 Hz or 512 Hz fork. The steam of the vibrating fork is placed on midline head. If the tone can be perceived by the affected ear, that is the indication of unilateral conductive hearing loss. If the tone is heard by the unaffected ear, that indicates the presence of unilateral sensorineural hearing loss.In Rinne test both air and bone tests are conducted. In air conduction, the normal volume tones are louder than by bone conduction. The bone conduction stimulus appears louder in conductive hearing loss cases. In cases of sensorineural hearing loss, the air conductions sounds appear louder even though both air and bone conduction sounds are lowered. If a 265 Hz fork is included in testing, the Rinne test is considered the most sensitive in mild conductive hearing loss detection.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...