ALS Disease FactsAmyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects the nerve cells that are controlling voluntary muscles. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a motor neuron disease and leads to degeneration of motor neurons that transmit messages from the brain to the muscles. This disease is also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease named after American baseball player who suffered from this medical condition.
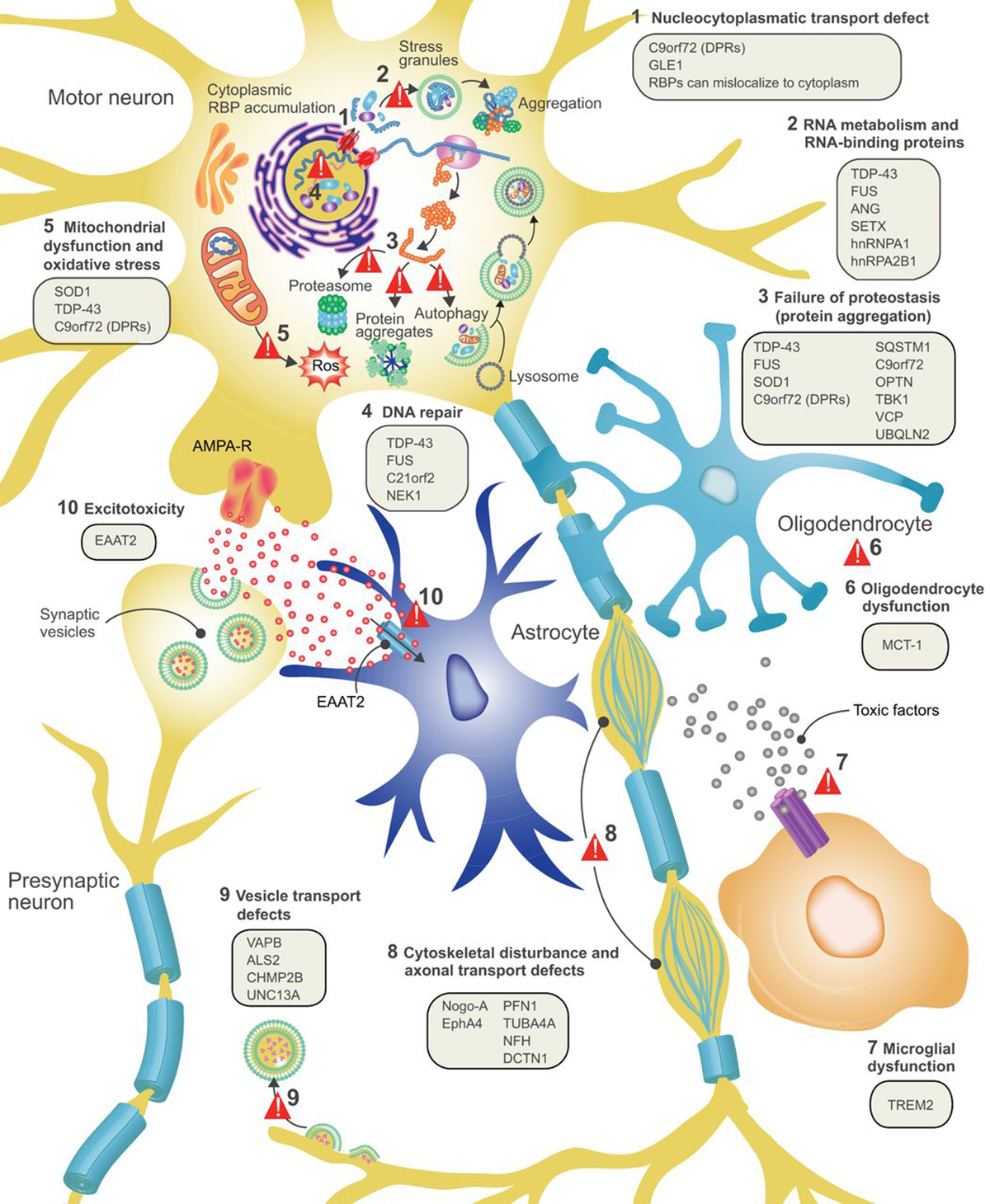
Causes of ALS As it was already mentioned, ALS disease is characterized by obstruction and destruction of message transmission between the nerves and voluntary muscles. However, the cause of ALS disease is not quite understood. Scientists believe that ALS disease is in most cases a genetic disorder and it is known as familial ALS. Another possible cause may be excessive levels of glutamate, a chemical that enables communication between neurons. Immune system may also be involved in development of ALS disease. All in all, any of these causes result in impaired and ruined communication between upper motor neurons located in the brain and lower motor neurons located in the spinal cord. As motor neurons degenerate they stop sending messages to muscles. Due to this, muscles become weak and stiff, and in time, as the disease progresses, muscles atrophy.
Symptoms of ALS DiseaseAt the onset of ALS disease the symptoms are very subtle and often overlooked. Depending on the progression of the disease, symptoms may vary from a patient to patient. People with ALS disease do not necessarily experience the same symptoms and the same sequences of progression. However, each affected person experiences muscle weakness and paralysis.
Initial symptoms commonly include muscle twitching, muscle atrophy and muscle cramps. Over time muscles become rigid. Muscles of the legs and arms are usually primarily affected. Sufferer may experience trouble walking, often tripping or stumbling, dropping things and can have difficulties in completing simple tasks such as writing, dressing, washing, or turning a key in a lock.
As the disease progresses, muscle weakness and atrophy spread to other parts of the body, such as face and torso. This results in difficulty swallowing and chewing. There may be also speech problems, and frequently, patients have slurred speech. Breathing muscles can be affected too which requires permanent ventilatory support for the patient in order to survive.
Diagnosis of ALS disease is based on tests to rule out other conditions. These tests include electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction velocity. Electromyography detects the nerve impulses within the muscles and nerve conduction velocity presents the speed communication between the nerves and muscles.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...