
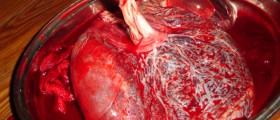
A molar pregnancy represents an abnormal development of placental tissue in the beginning of a pregnancy. Molar pregnancy can be complete and partial. In complete molar pregnancy there are only parts of the placenta and no fetus. This abnormal placenta grows and produces human Chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone normally synthesized during pregnancy and this is why there are symptoms of pregnancy even though the woman has not actually conceived. In complete molar pregnancy the sperm actually fertilizes an empty ovum. On the other hand, in partial molar pregnancy an ovum is fertilized by two sperms. In this case instead of normal development of twins the placental tissue does not develop adequately. This also refers to the fetus which is abnormal and suffers from many chromosome irregularities. The fetus has no chance of survival.
There are many reasons why molar pregnancy occurs. Some of the potential causes include certain defects of the ovum, abnormalities of the uterus, a diet low in proteins and fat and certain vitamins such as vitamin A.
Molar Pregnancy: Symptoms
The symptoms and signs of molar pregnancy are actually the same as in normal pregnancy during the first trimester. It features with a missed menstrual period, increased breast tenderness, morning sickness and fatigue. Apart from these relatively normal symptoms there are additional symptoms which are considered pathological. They include abnormal growth of the uterus, intensive and severe nausea and vomiting, vaginal bleeding, vaginal discharge which resembles grapes and general pelvic discomfort. Furthermore, a woman suffering from molar pregnancy may also develop symptoms and signs of hyperthyroidisms such as rapid heart rate, fatigue, weight loss, muscle weakness, heat intolerance and subsequent sweating, irritability, anxiety and enlargement of the thyroid gland. There are also symptoms similar to those in preeclampsia such as swelling of the feet, ankles and legs and high blood pressure. The symptoms that resemble those in preeclampsia occur during the first trimester and they are considered typical features of hydatiform mole.
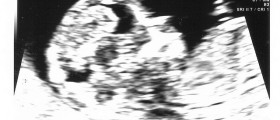
Molar Pregnancy: Diagnosis and Treatment
The doctor performs a pelvic exam and takes samples of a woman's blood which confirm increased levels of human Chorionic gonadotropin. Molar pregnancy can be easily diagnosed with the assistance of an ultrasound test.
The treatment for molar pregnancy includes removal of the abnormal tissues from the uterus. This removal includes a suction curettage. It is essential for a woman who has suffered from a molar pregnancy to undergo regular hCG blood test. This test may confirm or rule out the presence of interminable cell growth in a form of trophoblastic disease in the uterus. The tests are repeated every 6 to 12 months. In older women a molar pregnancy can be also treated with hysterectomy.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...