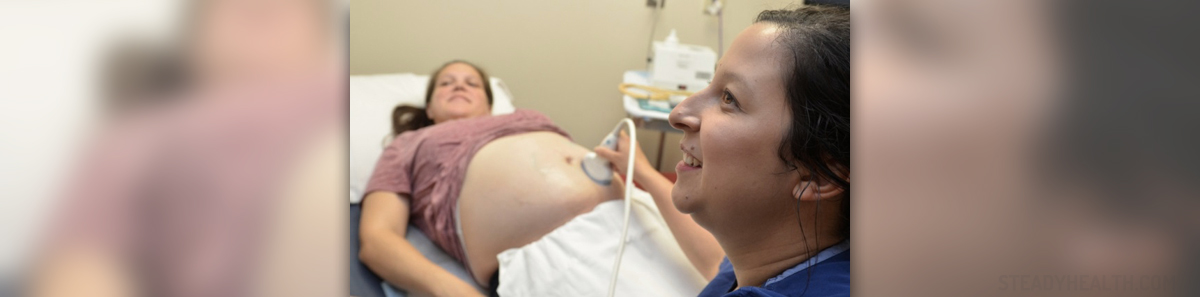
For most women, pregnancy is the happiest and the most exciting period of their lives. However, there are numerous physical and physiological changes that take place in a woman’s body during pregnancy. These changes are caused by hormones of pregnancy that play different roles during gestation weeks.
Beta Human Chorionic Gonadotropin HormoneBeta Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone (B-HCG) is one of the major hormones of pregnancy. The amounts of this hormone can be detected in home pregnancy tests. The secretion of b-HCG begins after the egg is implanted. It stimulates the corpus luteum to secrete estrogen, progesterone and other pregnancy hormones. This function is later performed by the placenta. In the second trimester levels of b-HCG considerably decline. Presence of beta human chronionic gonadotropin hormone can be also detected in individuals with testicular cancer.
Luteinizing Hormone
Luteinizing Hormone (LH) can be found in both men and women. It is produced by the pituitary gland. The main function of luteinizing hormone in women is to cause release of the egg from the ovary or the ovulation. LH helps to increase estrogen levels secreted by follicle cells. After the ovulation, luteinizing hormone converts the residual follicle cells into the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum secretes progesterone to prepare the inner lining of the uterus for implantation. During the first two gestation weeks LH maintains luteal function to enable constant and smooth production of eatrogen and progesterone. During pregnancy, function of LH hormone is controlled by b-HCG.
Follicle Stimulating HormoneFollicle stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates the maturation of the ovarian follicles in order to produce the egg. It also helps in the maturation of the residual follicle to the corpus luteum. It is also produced by the pituitary gland and it is the main hormone of an early pregnancy next to luteinizing hormone.
Progesterone
Progesterone is the main hormone of pregnancy that prepares the endometrium for implantation. It is produced by the corpus luteum. Progesterone acts by increasing the blood supply of the uterine wall and encouraging production of amniotic fluid that aids in growth of the embryo. Increased levels of progesterone during pregnancy prevent menstrual bleeding and release of additional eggs. Also, this hormone upholds functioning of the placenta and protects against damage to the fetus and placenta. Furthermore, progesterone stimulates the growth of the breast tissue but prevents lactation until childbirth. This hormone also strengthens the pelvic wall and prevents contractions of the uterus. Progesterone levels significantly decrease after childbirth.
Estrogen
Estrogen is produced by the corpus luteum and later this function is taken over by the placenta. Estrogen regulates production of progesterone and maintains uterine blood flow. This hormone is vital for fetal development. Estrogen regulates the bone density and proper growth of inner organs of the fetus.
Other Hormones during Pregnancy
Other pregnancy hormones are human placental lactogen, relaxin, erythropoietin, cortisol, oxytocin and prolactin. Hormone oxytocin is responsible for uterine contraction and stretching of the cervix during labor. Lactogen stimulates the production of breast milk.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...