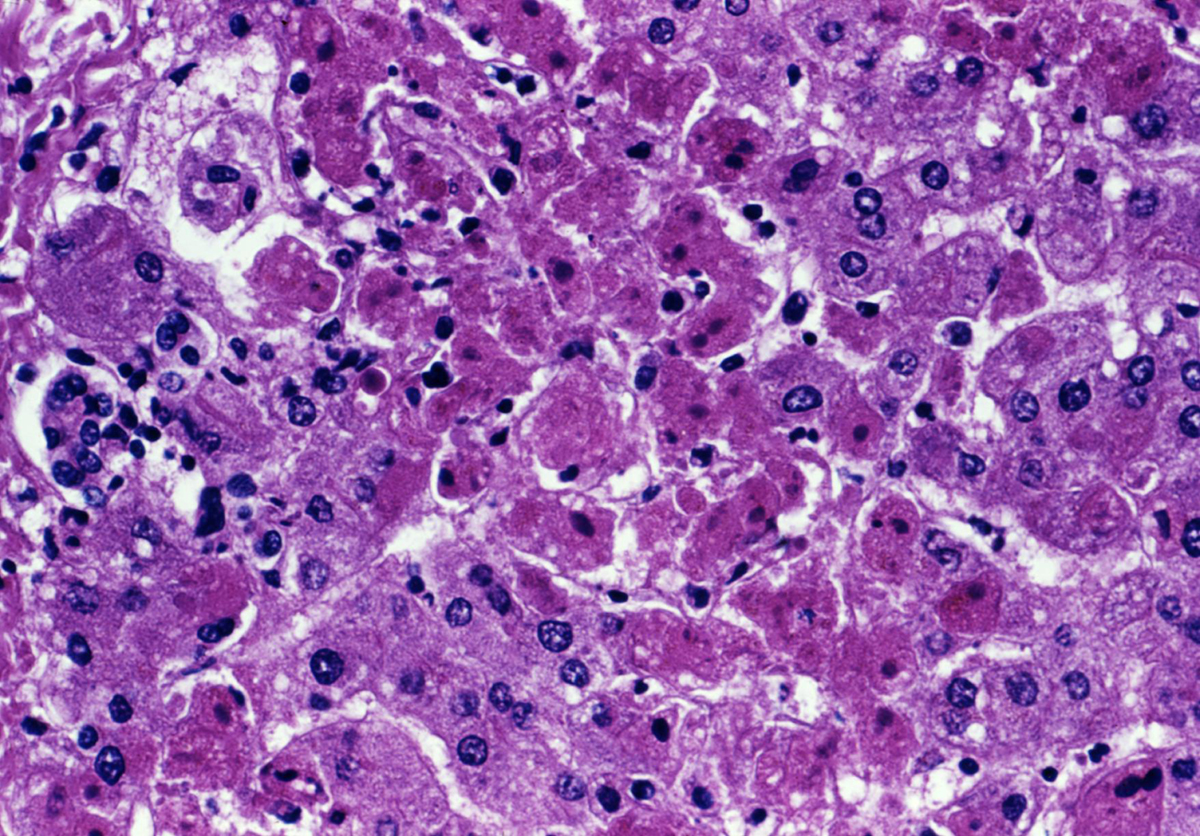
Liver Failure
Liver failure is impaired functional capacity of the liver which occurs as a result of acute or more frequently chronic liver disease.Causes of Liver Failure
The most common causes of lifer failure are viral infections, excessive alcohol intake, some medications or different metabolic disorders.Symptoms of Liver Failure
The most common clinical signs of liver failure are: jaundice, skin and endocrine manifestations, fever and septicemia, hematological disorders, neurological changes (Hepatic encephalopathy), hyper-dynamic circulation, ascites - fluid in the abdominal cavity and, expressed weakness. Skin changes that accompany liver failure usually include spider nevus or angioma, which are manifested in the centrally enlarged arterioles with fine radial branches. They are located on the face, neck and upper chest.Among skin symptoms, palmar erythema may occur and it is expressed as lipstick red palms. Also, flexion stiffness of 3. and 4. finger phalanx, hairy fingers, or loss of the nail root crescent may often be seen.
The safe endocrine disorders that occur as a consequence of liver failure include: testicular atrophy, loss of hairiness and gynecomastia - enlargement of milk glands in men, and menstrual cycle disorder in women.
Bleeding of the skin and mucous membranes of various organs occur as a result of haematological disorders. Airy hand tremor and fetor hepaticus (sweat smell of rotting) are the symptoms of precomatose state of the liver cirrhosis.
Acute liver failure (hepatitis fulminantly) is defined as acute weakening of liver function in patients who previously had healthy liver. Between the beginning of the first symptoms (malaise, jaundice), and different degrees of encephalopathy, coagulopathy, hypotension, fever, heart failure or oliguria (decreased urine excretion) with azotemia (presence of nitrogenous substances in the blood), goes from 2 to 12 weeks. Coma, hepatorenal syndrome, pancreatitis, massive gastrointestinal bleeding, and sepsis may lead to death.
Diagnosis
Establishing the diagnosis is based on anamnesis, clinical examination and laboratory findings which include reduced amount of albumin in serum, coagulation factors, cholesterol, and increased bilirubin values, high values of ALT and AST which indicate massive necrosis of hepatocytes.Treatment
Acute liver failure treatment is based on maintaining vital functions and prevention of brain edema, and is being implemented in intensive units. It is applied by intravenous giving mannitol, antimicrobial treatment, lactulose and infusion of amino acids. Ampoules of Flumazenil are useful in the treatment of encephalopathy.Treatment of slower disease progression requires an absolute ban on drinking alcohol, use of hepatoprotective drugs and input of large quantities of carbohydrates and protein in the diet. Patient’s nutrition should be balanced, containing enough vitamins, proteins, carbohydrates and fats. Heavy and prolonged physical effort should be avoided.
Liver transplantation is the most useful way of treatment, but in the case of short duration of acute liver failure this way of treatment may be unsuccessful.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...