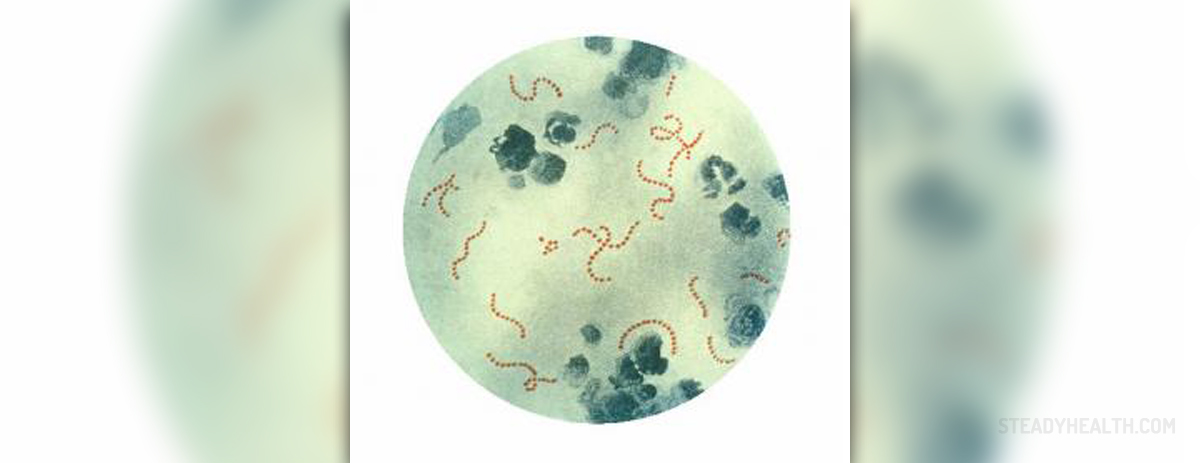
Group B Strep (Streptococcus) or GBS is a bacterial infection which usually affects pregnant women. The infection occurs in the lower intestine, vaginal or anal area and it can be passed on to the baby. In order to make the diagnosis the doctor will take a swab of vagina and rectum. The culture is then analyzed to determine if there is GBS. The results can be available within two days maximum. In some cases the bacteria can be found in males and females which are not pregnant.
GBS can colonize the gastrointestinal tract and in rare cases the respiratory tract without causing any symptoms or problems. However, if the infection spreads to the bladder or womb it can cause severe damage in adults disregard of the sex or pregnancy.
The prescribed treatment would usually be antibiotics which can also prevent the infection from spreading to the unborn baby. The treatment can be penicillin or ampicillin. In the past erythromycin and clindamycin were commonly given but it has been discovered that the bacteria are extremely resistant to these medications. In some cases they are prescribed if it is determined that they can be effective. Vancomycin can be the best choice if the patient is allergic to penicillin. Fluoroquinolones can also be useful. The newest antibiotic which has the ability to fight against GBS is linezolid.
It is important for your doctor to choose the best medications for you and to determine the length of the therapy. If you developed complications such as pneumonia, sepsis or sepsis arthritis, a surgery would be the adequate solution. Surgery is also recommended in cases of the infection of the soft tissues, discitis, necrotizing fasciitis, epidural abscess or osteomyelitis. In almost all cases of GBS it would be necessary to include different experts in various fields. This depends on your condition. A pulmonary lung specialist will have to treat lung problems, a cardiovascular expert will deal with heart and sepsis related complications, a rheumatologist will take care of soft tissue problems and an urologist will cope with the bladder and urinary infections. If the patient is a pregnant woman, she will need a gynecologist and if the newborn is infected with GBS a neonatologist will be required to determine the treatment. If GBS is passed on to the baby the symptoms can occur after few hours of delivery. The baby can have breathing problems, unstable blood pressure or kidney problems. Some severe complications can be pneumonia, meningitis or sepsis.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...