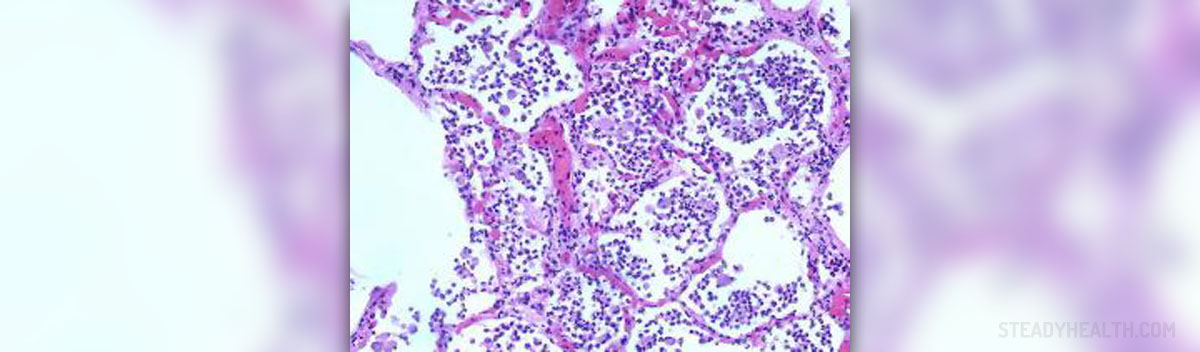
Acute Pneumonia
Acute pneumonia is acute inflammation of parenchyma of the lung, to be more precise alveoli of the lung. This inflammation is accompanied by accumulation of fluid in alveoli which leads to typical symptoms of pneumonia such as difficulties with breathing and in some cases shortness of breath.
Acute pneumonia may be caused by various infective agents or it may result as a consequence of injury. Acute pneumonia may lead to certain complications in elderly people and young children. These two groups require special care and attention when it comes to acute pneumonia.
Causes of Acute Pneumonia
Acute inflammation of lung parenchyma is most commonly caused by different infective agents including viruses, bacteria, fungi and protozoa. However, in majority of people acute pneumonia is caused by bacteria. The infection usually spreads from upper parts of the respiratory tract. Lower lobes of the lungs are predominantly affected by the process of inflammation.
Additional cause of pneumonia includes damage to lung tissue such as exposure to different irritants, chemicals and radiation. Aspiration of stomach acid may be another cause of acute pneumonia. Symptoms of Acute Pneumonia
The symptoms of acute pneumonia vary a lot and they are basically determined by the actual cause. Symptoms of bacterial pneumonia are rather different comparing to pneumonia caused by viruses. Still, acute pneumonia usually starts with symptoms which resemble symptoms of flu and influenza and further progression of the disease may include increased body temperature accompanied by chills, chest pain and difficulties with breathing including cough and wheezing. Since the infection first affects upper parts of the respiratory tract patients additionally complain about sore throat. Headache, rapid heart rate and profuse sweating may occur as well. If problems with breathing are severe one may develop peripheral cyanosis.
Treatment for Acute Pneumonia
Diagnosis of acute pneumonia can be set after chest X-ray, blood and mucus tests have been performed. The treatment is adjusted according to the cause of inflammation. Patients need to rest and stay in bed for certain period of time, drink lots of fluids and have balanced diet.
Bacterial pneumonia is treated with antibiotics. The most commonly prescribed antibiotics include penicillin, amoxicillin, erythromycin, clarythromycin, and so on. Which of antibiotics will be administered depends on the bacteria that led to infection. In case of viral pneumonia patients may be given rimatidine, amantadine, oseltamivir and zanamivir. Antibiotics are not administered in patients suffering from viral pneumonia unless they develop secondary bacterial infection.
In severe cases of pneumonia patients may be hospitalized and if the supply of oxygen is insufficient they are administered oxygen.
Complications of pneumonia such as pleuritis, pericarditis and endocarditis require further therapy with specific medications and patients are most commonly hospitalized. Complications usually affect people suffering from chronic diseases, elderly people and sometimes small children.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...