Strep A
The group A Streptococcus pyogenes (sometimes referred to it as GAS) is abacterium that normally lives on the skin and in the throat. Type A is mostlikely type to cause streptococcal infection but there are other lessinfective types as B, C, D and G strep bacteria. Infection may pass withoutany symptom or cause severe even fatal condition.
The bacterium is spreading among people when the secretions of the infectedperson get in contact with mouth, nose, eyes or wound of the uninfected person.Patients already ill or wounded are more likely to be infected.
Illnesses and complications
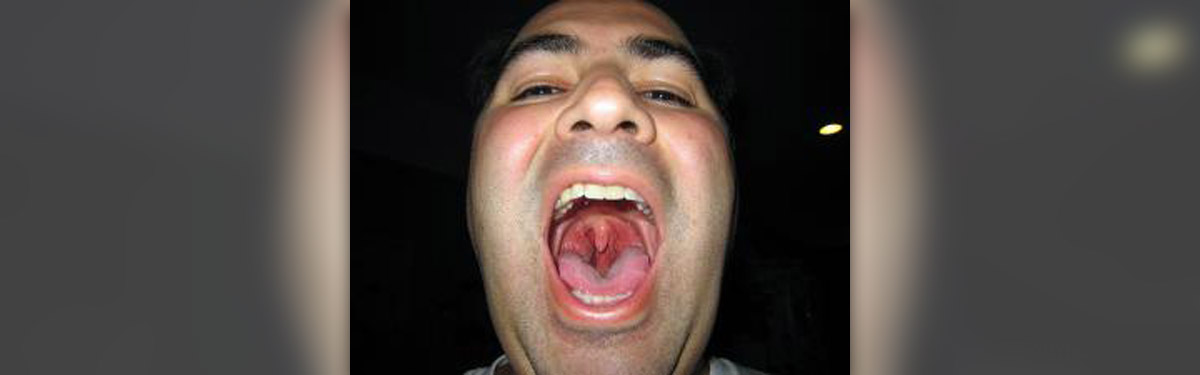
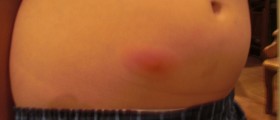
Strep A may cause different illnesses, from mild to serious. It could be thereason behind sore throat, impetigo, but also scarlet, postpartum (after birth)and rheumatic fever, pneumonia and wound infections.
There is a certain type, subtype of strep A, called invasive strep A. Thissubtype is responsible for necrotizing fasciitis and strep toxic shocksyndrome.
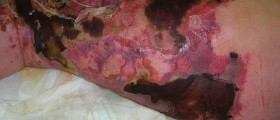
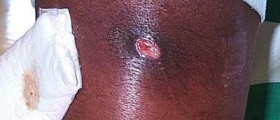
Necrotizing fasciitis is also known as "the flesh-eating disease".Strep A infects deep layers of skin and releases the toxin, destroying musclesand flesh. Early symptoms include pain, fever, heat, swelling and redness ofthe infected spot. In order to save patients’ life, sometimes is necessary tocut the whole muscle or entire extremity.
Strep shock syndrome is also progressive strep infection, where toxinsdestroy the tissue. Symptoms of strep shock syndrome are no different than anyother illness, and those are fever, dizziness and confusion. The conditioncould lead to extreme hypotension, shock, liver, kidney and lungs problems andmay even end fatally.
Possible complications may occur in strep A respiratory infections. One ofthem is acute rheumatic fever (ARF). The condition is frequent in developingcountries, but rare in the United States. It usually affects children 5 to 15years old, following the untreated pharyngitis, caused by strep A. The signs ofARF include: pancarditis, endocarditis, erythema marginatum (red rash on thebody and extremities), migratory polyarthritis of the joints subcutaneousnodules and sydenham chorea (neurological problems). Pancarditis (inflammationof complete heart tissue) is one of the most severe complications. ARF is notrheumatic heart disease: ARF is the acute inflammation and rheumatic heartdisease is a (non-inflammatory) sequel of ARF.
Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN) could develop after the strepskin infection or strep throat infection. Symptoms of PSGN are paleness of theskin, headache, lethargy, poor appetite and back pain. Patients might sufferfrom hypertension, edemas and have dark urine, because strep A affects the kidneys.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...