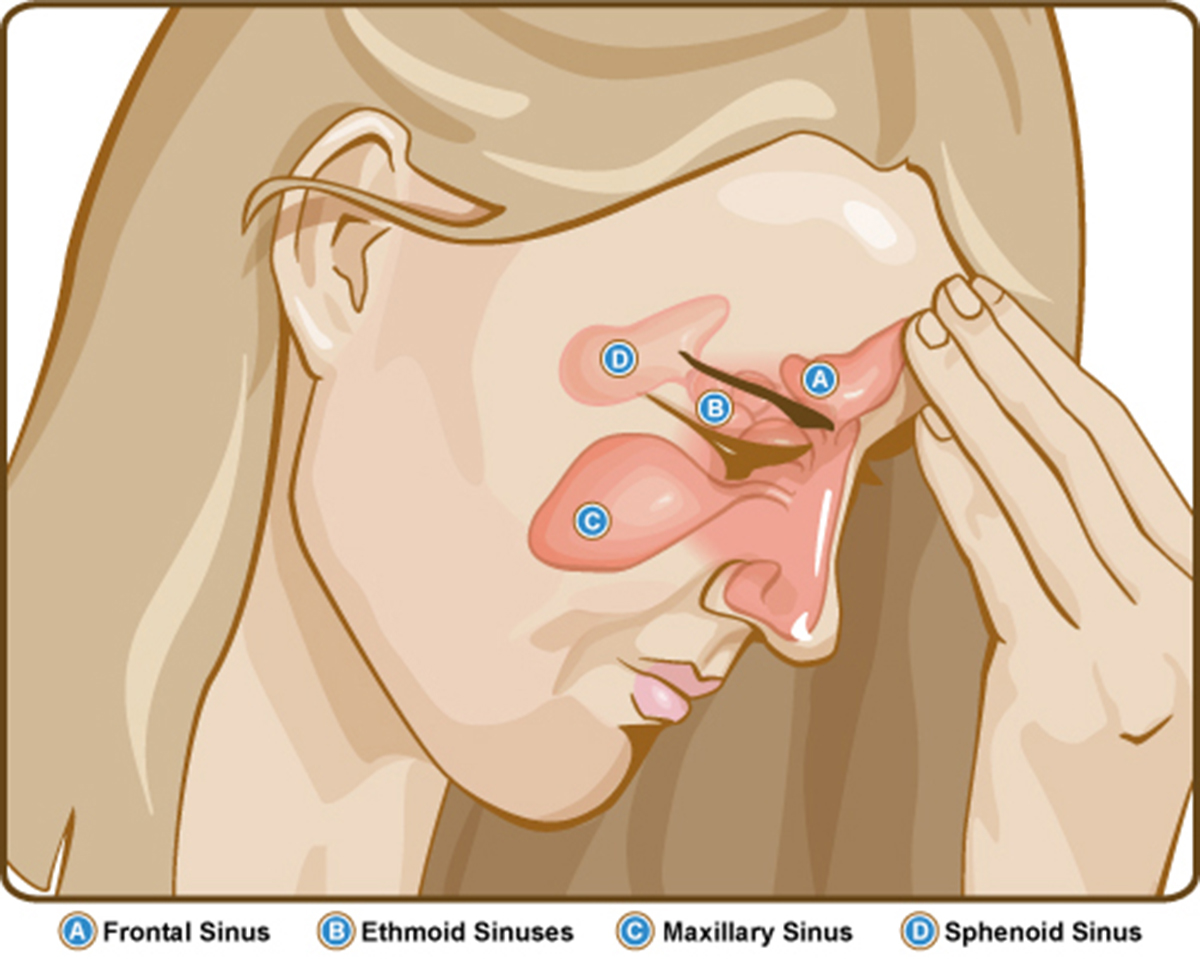
Sphenoid Sinusitis - Overview
Acute sphenoid sinusitis is a relatively rare inflammation of the sphenoid sinus. Chronic sphenoid sinusitis is, on the other hand, much more common. Still, no matter if the inflammation of this sinus is acute or chronic, it requires prompt diagnosis and treatment because if left untreated sphenoid sinusitis can lead to many serious complications. The sphenoid sinus is rather close to many vital vascular, neurologic, and optic structures and organs and the infection can spread from the sinus and affect some of them.
Sphenoid sinusitis used to be diagnosed only after certain complications have appeared. Today the availability of modern imaging methods such as CT scans or MRI can help faster setting of the diagnosis, and treatment can be highly effective with many antibiotics. Sphenoid sinusitis rarely occurs alone. It is usually a part of pansinusitis.
Causes of Sphenoid Sinusitis
The bacteria which cause sphenoid sinusitis differ from those which cause uncomplicated maxillary sinusitis. In maxillary sinusitis, the most common bacteria responsible for infection include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis.
On the other hand, acute sphenoid sinusitis is frequently caused by Gram-positive organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Chronic inflammation of this sinus may be caused by numerous bacteria, both Gram-positive and negative. Even anaerobes or mixed flora can be a cause of chronic sphenoid sinusitis.
The infection occurs due to improper drainage of the sphenoid sinus. Inadequate drainage is caused by anatomical differences which include variations in the position of the intersinus septum and small or abnormally placed ostia. Another cause of inflammation is blunt trauma and surgical trauma of the sphenoid sinus.
In some people, forceful entering of the water during swimming or diving may be another cause of sphenoid sinusitis. And finally, prolonged usage of steroids, diabetes, or radiation therapy may contribute to sphenoid sinusitis.
Symptoms of Sphenoid Sinusitis
The symptoms may be vague and not point to the exact location of the infection. Headache is a typical symptom of sphenoid sinusitis. The pain can be located at the vertex or be retrobulbar, parietooccipital, or frontal. Additional symptoms are fever and purulent rhinorrhea.
Hypoesthesia of the trigeminal nerve, together with neurologic and ophthalmologic findings, points to the presence of complications. The infection may spread onto the brain and cause meningitis, one may also develop abducens nerve palsy of hypoesthesia of V1 and/or V2. Chemosis, proptosis, ptosis, double vision, and the like are also complications of sphenoid sinusitis.
- Although relatively rare, complications of the inflammatory and infectious conditions of sphenoid sinusitis are the result of direct extension of disease to the surrounding tissues, or a propagated thrombophlebitis through valveless veins, which connect the paranasal sinuses with the orbit, cavernous sinus, and intracranial cavity.
- The spread of inflammation and/or infection from the sphenoid sinus to the orbit and cavernous sinus causes 5 distinct clinical entities: (1) preseptal cellulitis, (2) orbital cellulitis, (3) subperiosteal abscess, (4) orbital abscess, and (5) cavernous sinus thrombosis.
- The list of possible intracranial complications of sphenoid sinusitis includes meningitis, skull base osteomyelitis, and epidural, subdural, or cerebral abscess.
- A high index of suspicion must accompany any patient with unresolving sinusitis, increasing or changing symptoms, including the development of visual changes, ophthalmoplegia, focal neurologic signs, seizures, mood alterations, or persistent headache despite adequate therapy.
Differential diagnosis includes mucoceles, polyps, retention cysts, and fungal disease. The doctor may also suspect the presence of tumors of the nearby structures and salivary gland malignancies.
Treatment for Sphenoid Sinusitis
Treatment of sphenoid sinusitis is basically medicamentous and starts as soon as the diagnosis is set. Antibiotics and decongestants are always prescribed.
Surgery is engaged only if the condition does not respond to medications and if certain complications have occurred. The surgical approach includes opening the affected sinus, its drainage, and taking samples for the culture. Surgery for the sphenoid sinus basically includes open approaches such as external ethmoidectomy and transseptal approach.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...