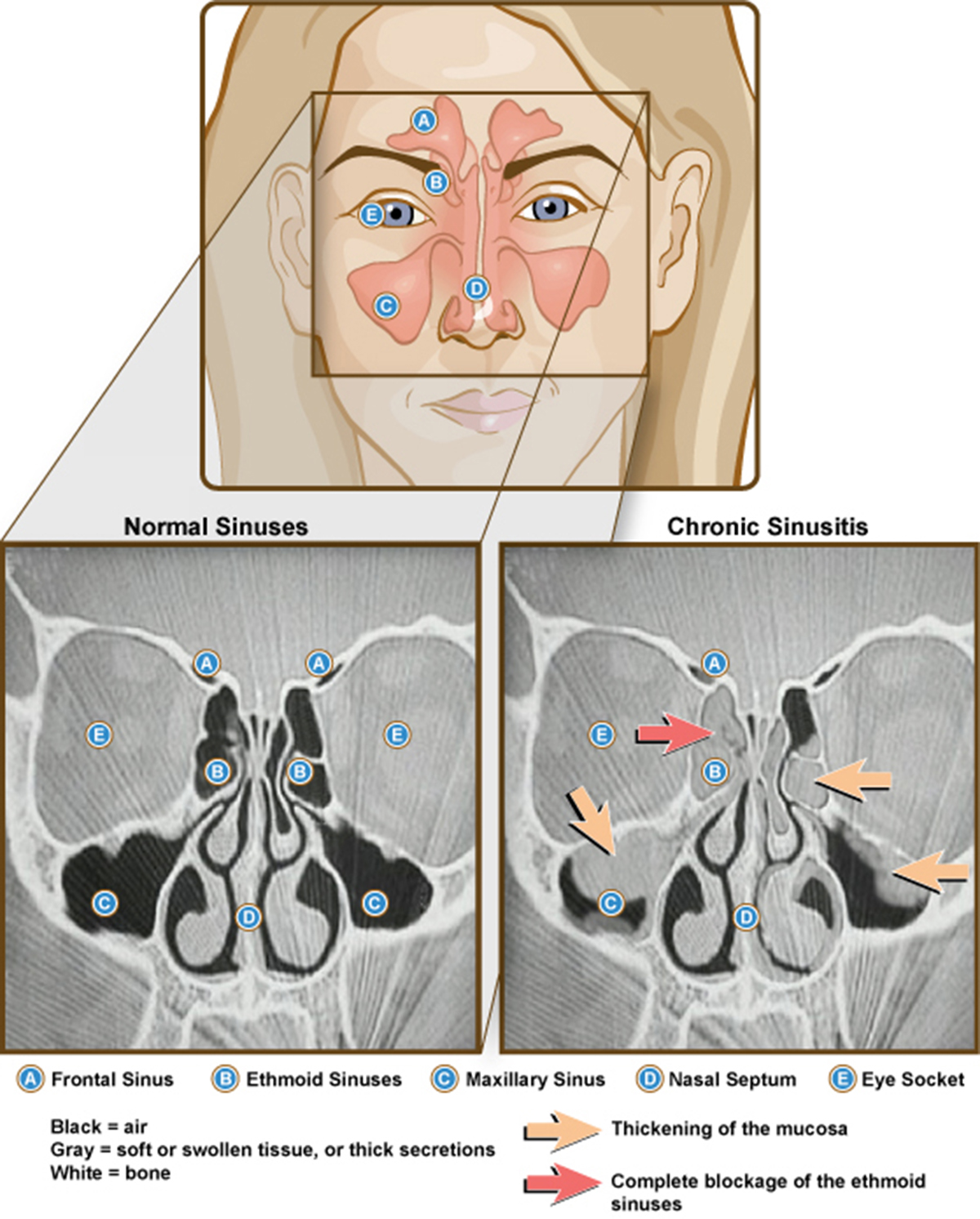
Sinusitis is the inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinus cavities. There are four groups of sinuses - maxillary, frontal, ethmodial and sphenodial. Para-nasal sinuses open into the nasal cavity and they are particularly susceptible to inflammation.
When the mucous lining of the sinuses gets inflamed, it swells and allows mucus to collect inside. This creates a favorable breeding ground for bacteria and it causes pain and pressure.
Causes of sinusitis
Sinusitis is often a consequence of an upper respiratory infection, such as common cold. It can also be caused by bacteria or it can be a complication from allergic rhinitis.
In order for the sinuses to function properly, the flow of the secretions must be normal and unobstructed. If the mucous linings swell, such normal flow is interrupted, which leads to sinusitis. The obstruction of sinuses and sinus openings can also occur due to certain activities, such as swimming or diving, and other possible causes include tooth infection, abnormal anatomy of the nose, polyps, trauma to the nose and foreign objects or particles.
Symptoms of sinusitis
Two main symptoms of sinusitis are pressure and pain. A feeling of pressure and stuffiness may extend all over the face, but it is usually located above the eyebrows, below the eyes and behind cheekbones. Pressure can become intense and grow into pain, which becomes worse if the head is moved or tilted forward.
Other symptoms may include fatigue, fever, nasal congestion, nasal discharge, sore throat, headache, toothache and ear pain.
Complications from sinusitis
If it is not treated properly and on time, sinusitis can evolve and cause complications. Those may include meningitis, brain abscess, osteomyelitis and ischemic brain infarction, orbital cellulitis and cavernous sinus thrombosis. All these conditions are very serious and potentially life-threatening.
Treatment for sinusitis
The first step in treatment of sinusitis is to eliminate organisms that cause the infection. In case of bacterial sinusitis, the treatment consists of antibiotics, such as amoxicillin, ampicillin, cefprozil or levofloxacin.
Since the symptoms will subside once the sinuses start draining, it is recommended to use nasal decongestants. They will also reduce swelling and edema. Topical decongestants are suitable for adults only and they should not be used for more than three days. As for the oral decongestants, they should be taken with caution by people who suffer from hypertension, because they cause contraction of the blood vessels.
Antihistamines can help in case sinusitis was caused by allergies and over-the-counter analgesics can be taken to relieve the pain.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...