
Dog and cat bites are the most frequent animal bites, and dog bites occurs much more often that cat bites. It is estimated that in 2007 in the United States five million animal bites were caused by dogs, 800,000 of which required medical assistance.
Persons who are bitten by animals are generally advised to seek medical attention. First aid for an animal bite a victim includes rinsing and covering with a sterile dressing. For rinsing, normal tap water is proven to be just as efficient as saline solutions.
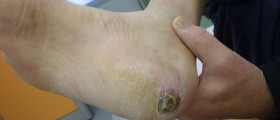
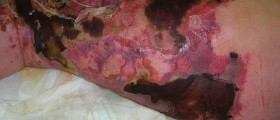
Upon arriving to an emergency room, the usual procedure includes inspection, cleaning, debridement and closure, although in some cases closure is contraindicated.
Inspection of the wound is done to examine the depth and extent in which the tissue has been damaged. This is usually done with local anesthetic, as it can be very painful.
Debridement means removal of devitalized, lacerated and otherwise damaged tissue that cannot be repaired. This is important for preventing a potential infection because necrotic tissue acts like a foreign body.
Irrigation is a way to clean the wound thoroughly. It is done with an irrigating solution, usually isotonic sodium chloride, which is cheap, safe and effective.
In a small number of bite wounds, when it is possible to clean the wound completely, primary closure is the viable option. Primary closure means that the wound is sutured right after inspecting and cleansing. Most of the wounds are best treated with delayed primary closure, which means the wound stays open for a few days covered with dressing.
If the wound is located on the hand, it may be immobilized with a splint or bulky dressing, in order to limit its use elevation is advised.
After treating the wound it is time to consider protection against rabies or tetanus. In some cases it is not known of the animal which afflicted the wound is vaccinated against rabies or not. Antirabies treatment is especially recommended if the animal in question is a fox, raccoon, bat or skunk.
Tetanus boost will be administered if the victim has not received even one ever or if it has been more than one year since the vaccine.
If there is abscess, sepsis or devitalized tissue, doctors usually order tests with aerobes and anaerobes cultures.
Some bites may cause bone fractures and if this is suspected, an X-ray can be performed to determine the damage to the bone.
Based on specific animals that inflicted the wound, antibiotics may be indicated as prevention.
Some wounds, especially those that are extensive, may require plastic surgery while the wounds to the skull require a consultation with a neurosurgeon.
In order to protect public health, all animal bite cases should be reported to local health authorities.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...