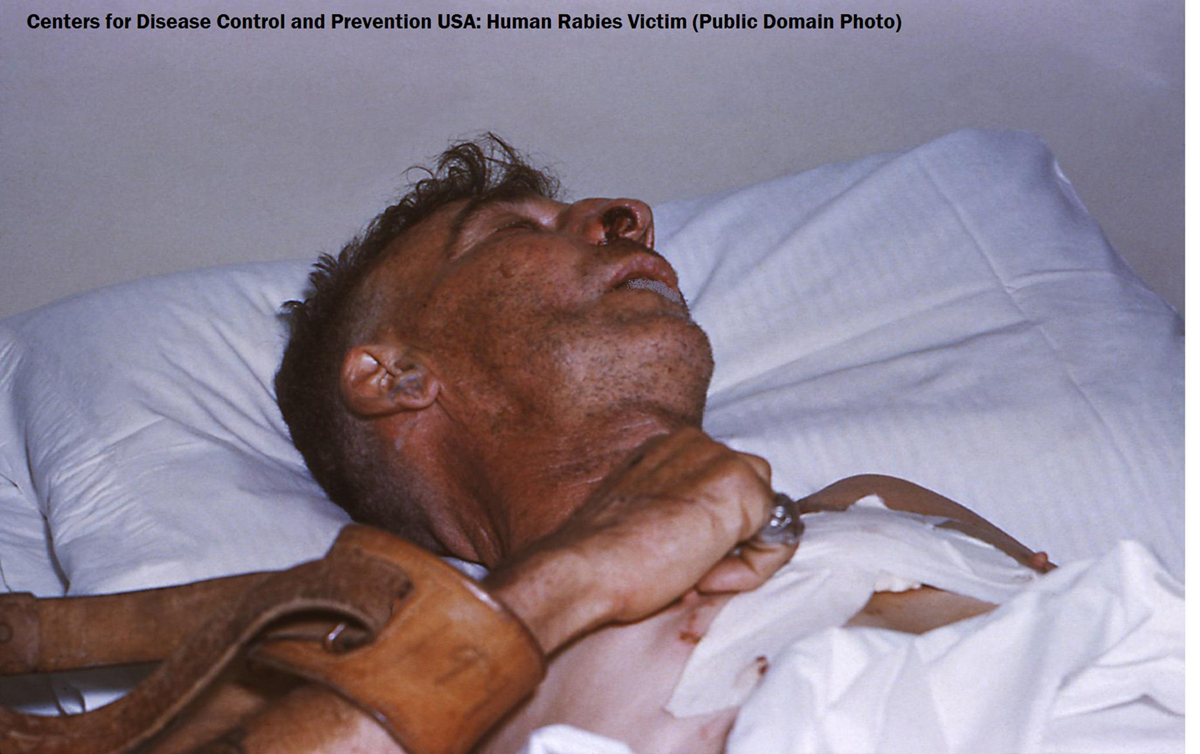
Rabies is a viral disease that mostly affects animals, both wild and domestic. Humans can be infected with the rabies virus if get bitten by infected animal. The virus is found in the saliva of an infected animal, so if its saliva gets in contact a person’s mucus membranes or broken skin like cut, scratch or open wound, it can lead to infection. Rabies is a disease that can be found in warm-blooded animals. Dogs are the most common carriers of the rabies virus. However, this viral disease is also often found in cats, sheep, horses, mules, goats, skunks, raccoons, bats, foxes and rodents. The rabies virus spreads through the central nervous system and leads to inflammation of the brain and spinal cord, a condition known as encephalomyelitis. In humans, the most noticeable symptom of rabies is the fear of water or hydrophobia. This causes an infected person to be horrified by the sight of water as well as to experience severe pain while drinking liquids, because of which a victim cannot quench thirst. Rabies is a lethal disease that results in a fatal outcome several days after the onset of the symptoms.
Symptoms of Rabies in AnimalsLearning to recognize signs and symptoms of rabies in animals can prevent spreading of the infection. Presence of the rabies virus in an animal is indicated by behavioral changes and other visible signs. There is a variety of signs and symptoms that accompany rabies, although sometimes the disease can manifest only in paralysis. Rabid dogs may exhibit changes in barking tone. Dilated pupils, refusing to eat or eating unusual substances can be also seen. Excess saliva accumulates in a rabid animal’s mouth and may drop uncontrollably.
Nocturnal infected animals may begin to appear during the day. Wild infected animals show fearlessness in the presence of humans. Rabid pets usually become aggressive and want to attack its owners or may be timid when approached. Other common signs in animals include: restlessness, disorientation, mood swings, lethargy, neck and throat paralysis and difficulty in drinking or walking. The incubation period typically lasts between 20 and 60 days. Death commonly occurs due to respiratory failure several days after the symptoms appear.
Symptoms of Rabies in HumansAfter the exposure to rabies virus, the symptoms in humans begin to appear after 2 to 3 months. However, sometimes it may extend to a year. Initial symptom of rabies in humans is burning sensation, numbness or pain around the area of animal bite. This is followed by flu like symptoms such as fever, sore throat, cough, runny nose and headache. Abdominal pain is also present. As the disease progresses, a victim starts to exhibit anxiety, restlessness, agitation, hallucinations and delirium. There are also face, neck and stomach muscle spasms accompanied by seizures. An infected person produces large amount of saliva and becomes unable to speak and swallow. Hydrophobia, paralysis of the neck and jaw and inability to drink come in the later stage of the disease. Eventually, a victim dies from the heart or respiratory failure.
Rabies Prevention and Treatment
Fortunately, rabies can be prevented with the rabies vaccine. Rabies vaccine can be administered to dogs, cats, horses, cattle and sheep. People working with animals must also receive preventive rabies vaccine. In case of infection, one must not wait for the symptoms to appear but needs to seek an immediate medical attention. The treatment involves wound care with soap and cleansers and injections of human rabies immune globulin.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...