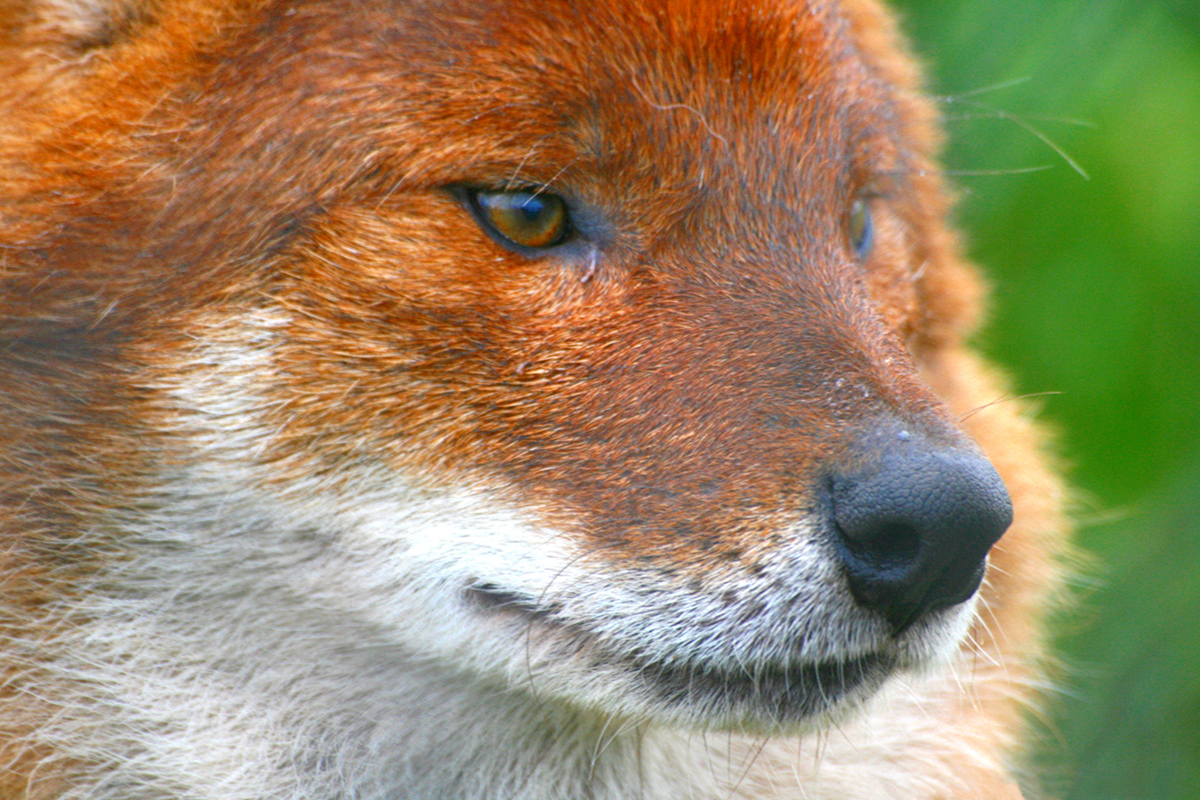

Rabies is a potentially deadly viral infection that affects humans and other mammals. The brain and the spinal cord are at risk when this infection strikes so it is important to react promptly to avoid the fatal outcome. Rabies is spread from rabid animals to humans usually through the animal’s saliva or brain tissue and rabid animal bites are the most common way to get rabies. In the U.S. bats, skunks, foxes, raccoons and coyotes are the most likely carriers of the virus causing rabies. Bats pose the greatest threat of giving the virus to people in the U.S. and Canada. Even though rabies are very rare in these countries any bites from animals need to be reported to medical professionals in case the treatment may be required.
Bat bites or scratches might go unnoticed since they are very small. Nevertheless, the person who has been in contact with the bat, may get infected. A rabid animal displays unusual behavior. If the animal shows no fear of humans that is usually shown by a wild animal; if it is excited, aggressive, restless and changes moods suddenly if it drools excessively, eats the things that are normally not eaten, or becomes active during the day (for animals that are usually active at night) if it is paralyzed it may be infected with rabies. The person who has been scratched or bitten by an animal should first wash the sore with soap and water and then call the doctor to determine if they have got rabies.
If the doctor suspects the animal that bit or scratched the person is rabid, they will administer the treatment immediately, because it is vital to treat the disease before any symptoms appear. It is too late to act after the symptoms develop, since the rabies virus damages the central nervous system, so the disease is almost always deadly. In most people symptoms of rabies appear within 2-3 months after they have been infected. Sometimes they appear only a few days after the contact with the rabid animal sometimes even a year later but the only way to prevent rabies is to seek medical care even if symptoms fail to develop.
Early symptoms of rabies can sometimes be mistaken for the signs of other conditions, because the infected person will feel pain, itching, burning or numbness in the area of the bite. Cough, sore throat, fever, pain in the abdomen, anxiety or restlessness are other signs that might be present while later symptoms may include anxiety, delirium, hallucinations, muscle spasms accompanied by seizures, fear of air and water; swings in blood pressure, temperature and pulse; paralysis, coma, and heart and lung failure.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...