A fairly common and, for most, an extremely embarrassing and awkward problem is the condition characterized by abrupt urge and need to visit the toilette, despite the fact that you have just had your go or had too little to drink. In medical terms, its main cause and culprit is the involuntary action of the muscle in the bladder’s wall, which causes the additional pressure resulting in contractions. Despite the fact that it can take over a body of any age, it most frequently is the biggest problem of the adults, or more specifically, of those who have reached the autumn of their lives.
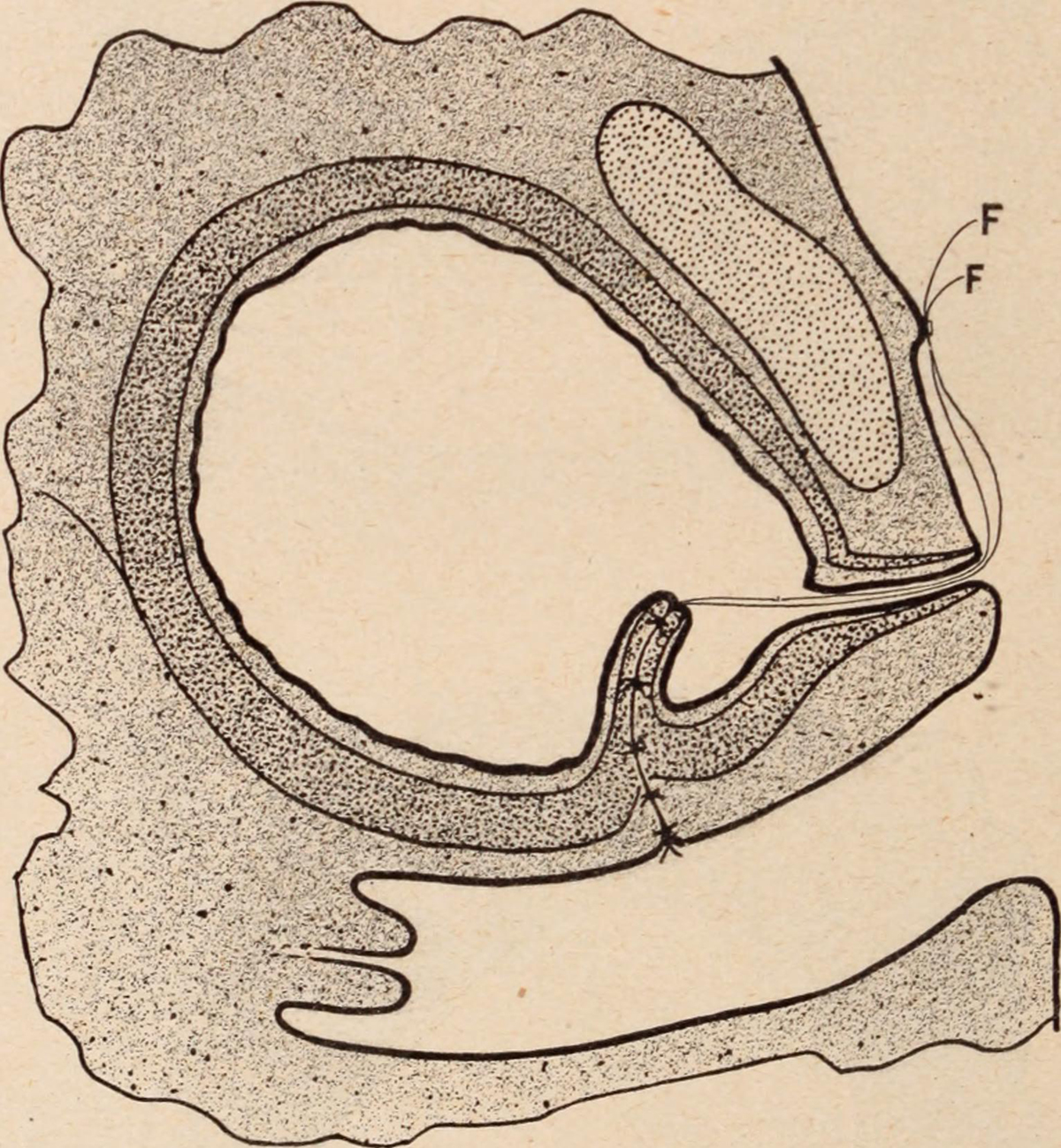
After examining the nature of this condition more in detail, the next which we should be acquainted with are the most common culprits which bring this condition about. At the top of the list are most certainly muscle spasms inside the bladder, but right after them, we find disorders of the nerves situated inside the bladder. Among all the muscles found in the bladder, probably the most important and most predominant is the one referred to as detrusor, which regulates the entire urination process. What is quite interesting is the role of our nervous system here – it regulates the way detrusor functions, i.e. when it actually contracts and when it relaxes, thus making this the most common cause of the hyperactivity of our bladder, without any regards for the quantity of liquid we have inside our bodies.
Couses
Furthermore, certain disorders and irregularities in the functioning of our nervous system can also be to blamed for the occurrence of this rather unbearable physiological condition, i.e. injuries to the spinal cord, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, multiple sclerosis, neuropathy diabetic in nature and heart conditions (primarily stroke). Since so many serious factors underlie this condition, people hope that there will be as many ways to treat it, but it is actually not the number of available treatments that plays a vital role, because the treatment depends on the characteristics and health condition for the person in question. The most general approaches include behavioral reprogramming, various drugs and medicines and probably the least favorable, surgical procedure.
Treatment
Other commonly used methods also include rehabilitation process of the muscles of the pelvis (especially favorable in younger women), but pelvic-floor electrical stimulation, behavioral therapies, bladder teaching and other techniques are also at disposal. Certain medications have also shown noticeable results, especially when combined with the afore mentioned behavioral therapies. This has provided fairly solid evidence when it comes to the ascent of the success bar on the treatment rate scale.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...