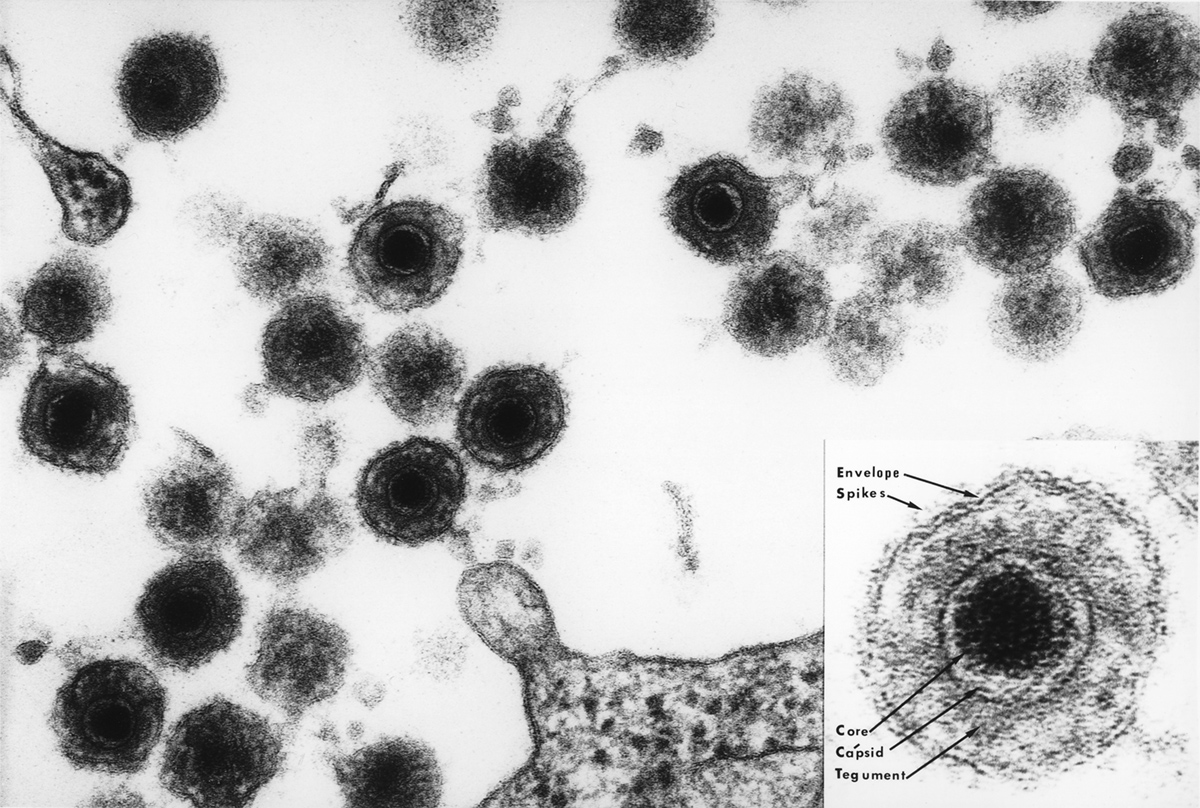
What is Mononucleosis?Mononucleosis or mono is a viral infection that is caused by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Infectious mononucleosis is often called kissing disease because the virus is transmitted through the saliva. This disease is not severe and not as contagious as common cold. Mononucleosis most commonly affects children and young adults. Children usually have mild symptoms and due to that the disease is often unnoticed. Older adults rarely get mononucleosis because they have antibodies against the virus. It is because they have been exposed to virus as a children and developed immunity to the virus. An affected individual may experience symptoms such as high body temperature, sore throat, weakness, malaise and swollen lymph nodes in the neck and armpits.
How does Mono Spreads?
Infectious mononucleosis is mildly contagious and it can spread through contact with saliva and mucus from the nose and throat. It is called kissing disease because it can be transmitted through kissing with infected person. However, it can be also caught due to exposure to cough or sneeze or a sharing glass, plate and other eating utensils with person that suffers from mononucleosis. You can also catch this virus if you exchange personal items such as tooth brush or towels with infected person. Among adolescents, mono is mainly transmitted through kissing, especially, deep kissing where the saliva is mostly exchanged. Another way to transmit infectious mononucleosis is to shake hands with other person after touching the mouth or nose.
Mononucleosis can be transmitted while the symptoms of the disease are present. When person recovers from mono, the virus remains inactive inside the body. The virus can become active from time to time but may not be followed by any symptoms and that is why sometimes people spread the virus unintentionally. Mononucleosis can be contagious for few weeks. Personal hygiene is vital in prevention of this disease.
Symptoms of Mononucleosis
The incubation period for mononucleosis is usually between four and six weeks. After incubation period, the symptoms start to appear. Initially an infected person feels general malaise, fatigue and chills. Loss of appetite is usually also present. After a few days, affected individual may suffer from severe sore throat, swollen tonsils, headache, fever and swollen lymph nodes. In about 50% of people with mono, the spleen may become swollen or enlarged. If symptoms last for longer period of time or appear frequently, you should visit your doctor. Chronic mononucleosis is characterized by the symptoms that last longer than six months.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...