Infectious mononucleosis is an infectious clinical syndrome caused by Epstein Barr virus. The main symptoms include fever, pharyngitis and lymphadenopathy usually of the neck, and enlargement of spleen or liver. Tiredness is usually present and it can sometimes lead to prostration. Epstein Barr virus is spread through direct contact with bodily secretions, mainly oropharyngeal secretions. Coughing, sneezing or kissing can be a way of transmission. Extremely rarely it can be transmitted via blood transfusion.
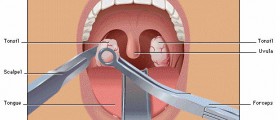
The infection is spread into lymphatic organs such as peripheral lymph nodes (usually of the neck but inguinal nodes can be affected as well) and the spleen. Liver, even though not representing a lymphatic organ, is commonly affected too. These organs become enlarged sometimes they even double. Enlargement of cervical lymph nodes can lead to difficulties connected to swallowing, rarely to problems with breathing. The role of T-lymphocytes is essential for clinical expression of the disease.
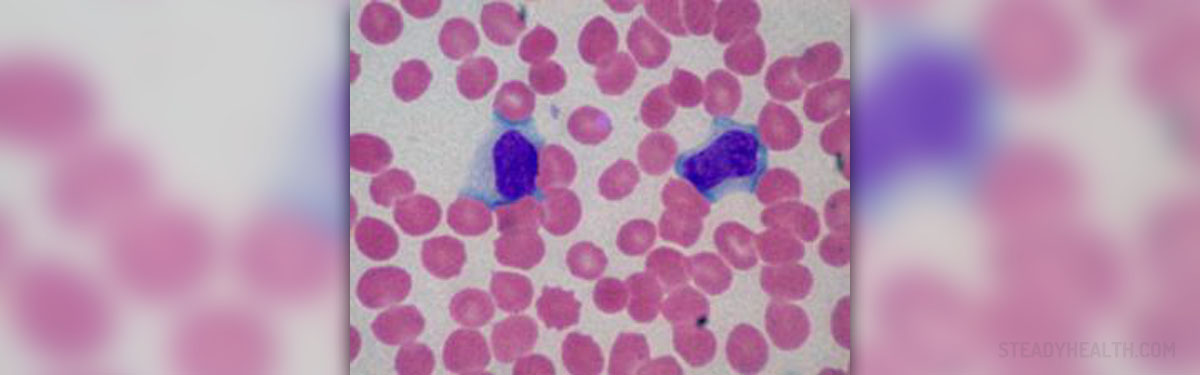
Some cases are mild and resemble simple cold therefore they are not even recognized as infectious mononucleosis. Others require hospitalization due to the severity of the symptoms.
Treatment Options for Infectious Mononucleosis
The treatment includes bed rest in most of the cases. Since the infection is caused by viruses no medications are required. Only those for reduction of high temperature can be used but your doctor will decide which ones. Some like Aspirin must not be prescribed to children under the age of 7 because of a serious condition called Reye's syndrome can occur.
Corticosteroids are indicated for airway obstruction due to extreme tonsil enlargement. Recovery period lasts approximately few weeks. After that, patients are recommended to keep away from sports activities for at least three weeks up to a few months, so as to not exhaust themselves. This is especially important for those previously experiencing enlargements of the spleen and liver.
Infectious Mononucleosis Complications
There are certain complications which can occur during the infection or after. The most serious is a spleen rupture. Enlarged spleen is susceptible to rupture. Therefore while palpating the spleen doctors have to be more careful. Those patients need to keep away from physical activities much longer that those without spleen enlargement. The condition is treated surgically. In extreme cases, encephalitis or myocarditis can result from the condition.
Later complications may lead to development of Peripheral T-cell lymphomas disorder and hepatic necrosis. These two are associated with the patient having a previous organ transplantation. Hodgkin and Non- Hodgkin lymphomas are reported to occur if patients have had Infectious Mononucleosis. There are researchers which have proved the connection of previous infection and onset of Burkitt's lymphoma.
- Serious complications during the acute phase of primary EBV infection are rare.
- Complications that occur in at least 1% of patients are: airway obstruction because of oropharyngeal inflammation, streptococcal pharyngitis, meningoencephalitis, hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia.
- Splenic rupture occurs in












Your thoughts on this
Loading...