
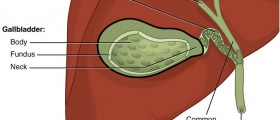
The gallbladder is a hollow organ with muscular walls which is used for the storage and concentration of bile. The gallbladder is positioned underneath the liver can store about 50 ml of bile. Its function is to assimilate inorganic salts and water out of the bile and that process multiplies the bile concentration. Due to its muscular wall, the gallbladder can compress and in that way release the liquid into the bile duct from where it goes into the duodenum.
Disorders connected with the gallbladder may result in very serious complications. These disorders are often connected with one's body due to reasons like irregular eating habits, obesity and hereditary factors. It is still unclear what signals the start of gallbladder issues, and sometimes even small infections can trigger further development.
A gallstone is very frequently the basis of a classical gallbladder issue. A gallstone is made of a consolidated crystalline matter made of cholesterol, calcium, blood, and bile which is formed in the gallbladder from where it travels into the bile duct and further where it causes the problems due to smaller canal dimensions.
Gallstones often get stuck and block the bile stream. “Cholelithiasis” is a word that is used in the medical world to describe the state of a gallstone’s existence, while the word “cholecystitis” stands for an inflamed gallbladder. Gallstones often occur in states like anemia or with liver diseases. Jaundice is often caused by gallbladder situations. The main characteristics of jaundice are yellow skin color, white mucus membranes and eyes color and infections of blood tissues. One of the bile’s functions is to decompose fat particles in food and to help to digest it, so when the gallbladder is not working properly, the food remains undigested. Gallbladder issues may also affect the blood pressure and heart rate.
Symptoms of gallbladder problems are not characteristic and they are often inter-worked with other digestive symptoms, so they can develop for years before they are recognized. The most indicative symptoms are pain underneath the rib cage on the right side, stools with a light or chalky color, food digestion difficulties (most notably grease or fat), nausea, gas, burping, bloating in the stomach, diarrhea, and constipation. It is not obligatory to have all the symptoms, but the more of them one has, the greater the ability to pinpoint the gallbladder problems more precisely.
Gallbladder attack symptoms include pain under the right ribcage which transfers to the back or the right shoulder, biliary colic (strong abdominal pain), nausea, gas, and vomiting. Attacks often happen at night or after a strong meal, pain worsens after deep breathing as well. These symptoms are provoked by gallbladder stones in most cases.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...