
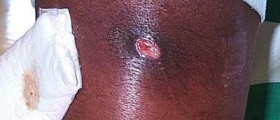
Fungal infections, also known as mycosis, are medical conditions caused by fungi that pass the resistance barriers of the body. Fungi usually live on dead layers of human skin, and they are literally all over the environment. They reproduce through microscopic spores in the air, and people often inhale them, or they land on the human skin. Fungi thieves and grows in dark and moist places, in hot and humid climate, and in crowded conditions. Human feet provide the perfect environment for fungal infections, as the skin sweats a lot and the anterior of shoes and socks provides darkness and warmth.
Athlete's Foot
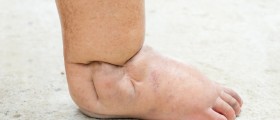
Athlete's foot is among the most common fungal infections. It is also known as the ringworm of the foot, tinea pedis or Hong Kong foot. The disease is caused by fungi in the genus Trichophyton and people usually get infected if they are walking barefoot in the moist areas – around the swimming pools, for example. The infection is normally accompanied by scaling, flaking, and itching of the affected skin. Sometimes, the blisters and cracks may also develop. The skin between the toes is most commonly affected, and it appears inflamed and very painful. In some cases, the infection may spread to other areas, such as the groin, for example.
Nail Infections
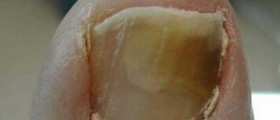
Fungal nail infections are usually spread from fungal skin infections. For example, patients with athlete’s foot will probably develop an infection on the toenails. Nails that have recently been damaged are more likely to become infected. Patients with other health conditions such as: diabetes, psoriasis, poor circulation, compromised immune system or general poor state of health are at increased risk of developing fungal nail infection. Infected nails usually look thickened and discolored. The nails often get a greeny-yellow color, and bright patches may appear where the nail has come away from the skin under the nail. Gradually, the nail becomes soft and may crumble and eventually fall off. Prevention and treatment
Fungi that cause fungal infections of the foot usually live on shower floors, wet towels and in footwear. These fungi spread from person to person if they are sharing showers, towels and footwear. Proper hygiene is a key to prevention. One should try to keep the feet and footwear as dry as possible and avoid walking barefoot or sharing showers and towels with other people. Treatment usually includes various over the counter antifungal creams and ointments. In most cases, foot hygiene is all that it takes to completely get rid of the infection.







_f_280x120.jpg)



Your thoughts on this
Loading...