
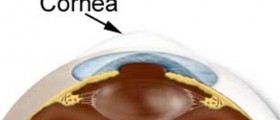
The pressure inside the eyeball is maintained within normal range by continuous and balanced production of the aqueous humor and its elimination from the eye into the systemic circulation. The aqueous humor is of great importance for nourishing the cornea, iris and lens of the eye. Namely, it contains all the necessary nutrients.
Apart from that, the aqueous humor is also significant for maintaining the shape of the eye. The pressure inside the eye remains normal in case the amount of produced aqueous humor is the same as the amount of drained aqueous humor. However, any imbalance that leads to either increased production or reduced elimination of this fluid may eventually result in elevated eye pressure. On the other hand, insufficient production of this precious fluid may also cause certain health problems.
Changes in Eye Pressure and Associated Symptoms and Signs
Normally, eye pressure ranges between 12 and 21 mm Hg. Pressure above 21 mm Hg is considered elevated while if it is below 12 mm Hg, it is known as low eye pressure. There are certain physiological changes which may only briefly cause a drop or increase in eye pressure. In case such abnormalities remain and linger for some time, certain parts of the eye may suffer damage of different degree.
Elevated eye pressure (ocular hypertension) develops due to increased production of the aqueous humor or its insufficient drainage into the systemic circulation. Such increase is typically accompanied by acute or chronic pain in the eye and headache. Additionally, there may be redress of the eyes and blurred vision. A medical condition characterized by an increase in the ocular pressure is known under the name glaucoma. If increased pressure remains and is not treated, it may cause severe and sometimes irreversible damage to different parts of the eye, especially the optic nerve.
Low eye pressure (ocular hypotony) may include persistent eye pain and even lead to serious complications such as retinal detachment. Blurred vision, swelling around the eyes, excessive tearing and reddening of the eyes are several more symptoms and signs caused by ocular hypotony.Treatment for High/Low Eye Pressure
Treatment for inadequate eye pressure generally depends in the underlying cause and is practically individual. A well experienced ophthalmologist performs ocular examination, measures the eye pressure and after identifying the underlying cause either prescribes some medications (eye drops, ointment etc.) or refers a patients to a surgeon. The best results are achieved if treatment starts on time. This way the underlying condition can be brought under control and potential complications may be successfully prevented.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...